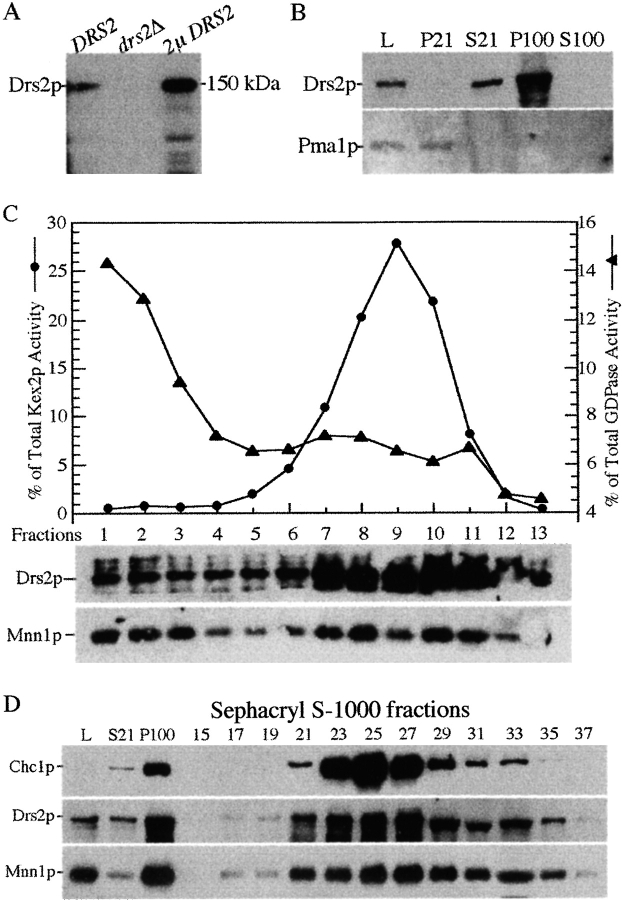
Figure 7.
Drs2p cofractionates with high-density membranes containing the late Golgi markers, Kex2p and Mnn1p. (A) Specificity of the Drs2p antibodies. Wild-type, drs2Δ, and SEY6210 pRS425-DRS2 (2μ DRS2) cells were grown at 30°C before lysing with glass beads in SDS-urea sample buffer. Total cellular proteins (0.1 OD per lane) were subjected to SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with affinity-purified antibodies against Drs2p. (B) Wild-type cells grown at 30°C were lysed (lysate, L) and subjected to centrifugation at 21,000 g for 30 min to generate pellet (P21) and supernatant (S21) fractions. The S21 fraction was further centrifuged at 100,000 g for 80 min to generate pellet (P100) and supernatant (S100) fractions. 20 μg of total protein per fraction was immunoblotted for Drs2p and the plasma membrane ATPase, Pma1p. (C) Wild-type cells grown at 30°C were lysed and subjected to differential centrifugation and sucrose gradient fractionation of the P100 fraction. These gradient fractions have been previously used to examine Mnn1p distribution in Figure 6 a of Reynolds et al. 1998. Equal volumes per gradient fraction were assayed by enzyme activity for Kex2p or GDPase and by immunoblotting for Drs2p, Mnn1p, and Pep12p. (D) Wild-type cells were grown at 30°C, lysed, and subjected to differential centrifugation to produce a P100 fraction, which was then subjected to gel filtration chromatography as described in Fig. 6. Samples of every other fraction from fraction 15 to 35 were assayed by immunoblotting for the clathrin heavy chain (Chc1p), the late Golgi protein Mnn1p and Drs2p.