Figure 9.
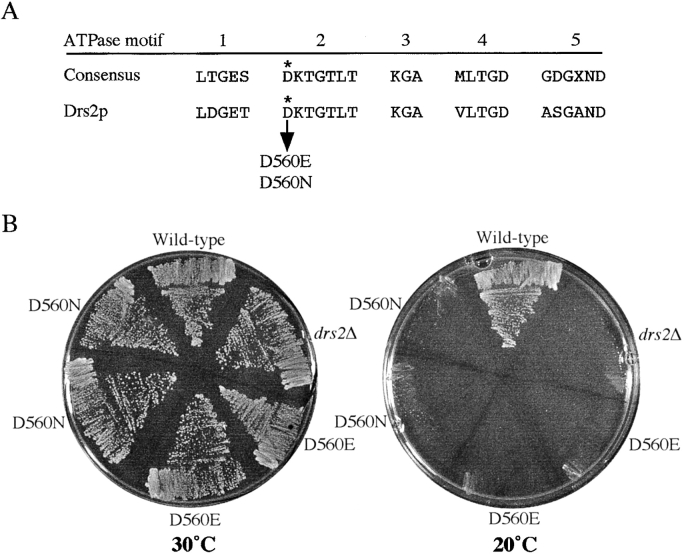
Mutation of a conserved ATPase motif causes loss of Drs2p function in vivo. (A) Comparison of five conserved consensus motifs of yeast P-type ATPases and the corresponding sequence in Drs2p (adapted from Catty et al. 1997). The arrow indicates the aspartic acid residue (D) at position 560, which was mutated to glutamic acid (E) or asparagine (N). (B) The drs2Δ strain containing plasmids pDRS2(D560E), pDRS2(D560N), pRS315-DRS2 (wild-type), and the pRS315 empty vector (drs2Δ) were grown at 30° or 20°C for 3 d.