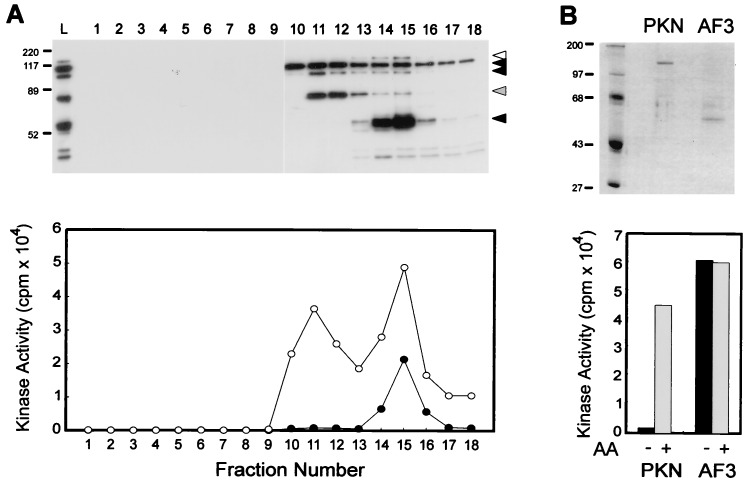
Figure 4.
Generation of constitutively active kinase after caspase-3-mediated proteolysis of PKN. (A) Mono Q column chromatography of the in vitro cleavage products of PKN. Baculovirus-expressed His-GST-PKN was digested with His-caspase-3, and the cleavage products were separated by Mono Q column chromatography. Each fraction was subjected to immunoblotting with αC6 (Upper) and the kinase assay in the presence (○) or absence (•) of AA (Lower). L indicates the sample loaded to the column. Positions of uncleaved and cleaved proteins are indicated with black and white arrowheads, respectively. Gray arrowhead indicates a cleavage product detected only in the in vitro reaction. (B) comparison of kinase activity between the recombinant full length PKN and its mutant AF3. PKN-FLAG (PKN) and AF3-FLAG (AF3) expressed in COS-7 cells were purified by anti-FLAG column, then equal amount of the proteins were subjected to SDS/PAGE followed by Coomassie brilliant blue staining (Upper) and the kinase assay in the presence or absence of AA (Lower). The results are representative of three independent experiments. Molecular mass markers in kDa are indicated on the left of the gel.