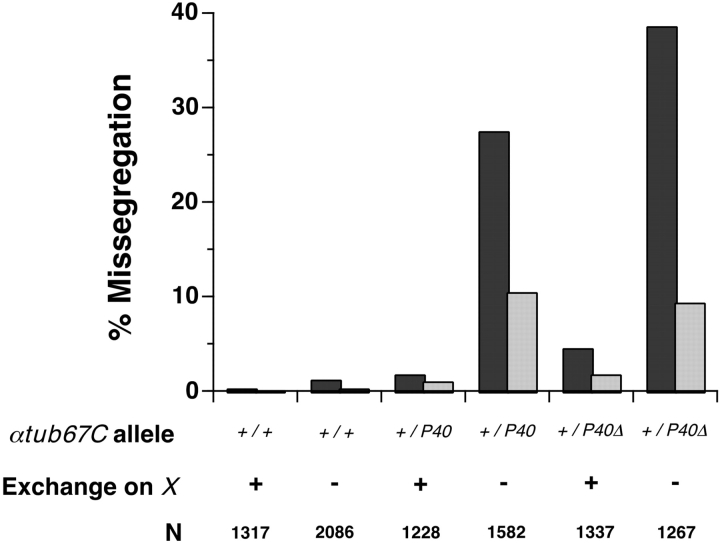
Figure 4.
The αtub67CP40mutation leads to elevated levels of achiasmate chromosome missegregation. The frequencies of X (dark bars) and 4th (light bars) chromosome missegregation (nondisjunction) are displayed for various genotypes. The genotype at the αtub67C locus is represented as: +/+, two wild-type copies of the αtub67C gene; +/P40, heterozygous for the αtub67CP40 mutation; and +/P40Δ, heterozygous for the αtub67CP40 mutation. These experiments were done in both X/X and X/FM7 females, allowing us to examine segregation in oocytes with (+) or without (−) exchange on the X chromosome, respectively. N is the adjusted total of progeny scored (Hawley et al. 1993). Chromosome segregation was monitored by methods outlined in Hawley et al. 1993 and Sekelsky et al. 1999. Although females homozygous for αtub67CP40are sterile, αtub67CP40Δ/+ females are fully fertile and viable.