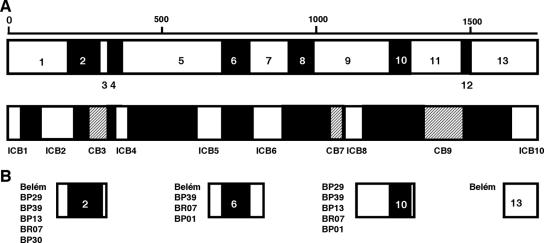
FIG. 1.
Schematic representation of PvMSP-1 and the recombinant antigens used in this study. (A) The PvMSP-1 protein sequence comprises seven conserved blocks (amino acid similarity among PvMSP-1 allele products of 71 to 85% [represented as open boxes]) and six variable blocks (amino acid similarity of 21 to 34% [represented as black boxes]) described previously by Putaporntip et al. (27). For comparison, we also show the original division of PvMSP-1 into interspecies conserved blocks (ICB) (amino acid similarity of >48% in pairwise comparisons of MSP-1 orthologs of P. falciparum, P. vivax, and Plasmodium yoelii [represented as open boxes]), conserved blocks (CB) (amino acid similarity of >50% between P. falciparum and P. vivax but lower in other pairwise comparisons [represented as hatched boxes]), and polymorphic blocks (amino acid similarity of <45% [represented as black boxes]) (5). These two ways of portioning PvMSP-1 differ in that Putaporntip et al. (27) made intraspecific-sequence comparisons, while del Portillo et al. (5) made sequence comparisons among species. Recombinant antigens used in previous studies are often named after interspecies conserved blocks (17, 24, 25, 32); for example, ICB2-5 comprises blocks 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 defined previously by Putaporntip and others (27). (B) Location of the 16 recombinant antigens used in this study. Note that antigens corresponding to variable domains of PvMSP-1 comprise stretches of conserved flanking sequence. Block 13 antigen corresponds to ICB10, the C-terminal 19-kDa fragment of PvMSP-1.