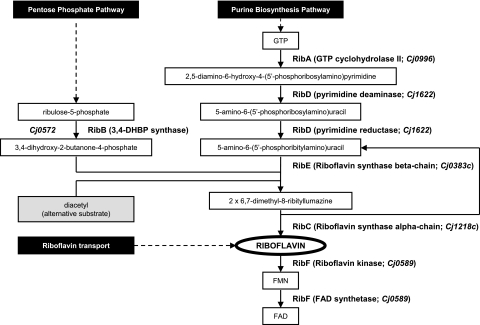
FIG. 1.
Overview of the different enzymatic steps in the riboflavin biosynthetic pathway resulting in the biosynthesis of riboflavin and the coenzymes FAD and FMN. Two distinct branches of the pathway interact at the formation of 3,4-dihydroxy-2-butanone-4-phosphate (DHBP), which undergoes condensation with 5-amino-6-(5′-phosphoribitylamino)uracil to yield the riboflavin precursor 6,7-dimethyl-8-ribityllumazine. One molecule of riboflavin is formed from one molecule of GTP and two molecules of ribulose-5-phosphate in a series of enzyme-catalyzed reactions. The enzymes and corresponding genes listed are those generally found in E. coli (2, 37). The Cj gene numbers given with the RibA, RibD, RibE, RibC, and RibF steps are based on the annotation of the C. jejuni genome sequence (17, 24) and require experimental validation. The mechanism whereby the DHBP analogue diacetyl can complement an ribB deficiency is indicated by the gray box.