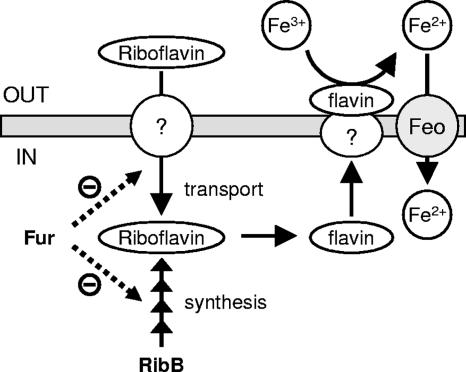
FIG. 5.
Graphic representation of our hypothetical model illustrating the proposed links among riboflavin biosynthesis, assimilatory ferric reduction, and iron acquisition in C. jejuni. Riboflavin biosynthesis via RibB (Fig. 1 and 2) or riboflavin uptake (Fig. 3) allows the activation of an as-yet-unknown flavin/ferric reductase, which mediates extracellular or membrane-bound reduction of ferric iron (Fe3+) to ferrous iron (Fe2+) (Table 2) (9, 15, 29). Ferrous iron may subsequently be transported by the Feo ferrous iron transporter system (Fig. 4) (22, 36). The ferric uptake regulator Fur is depicted as a negative regulator both of riboflavin synthesis and of an uncharacterized riboflavin uptake mechanism (Fig. 3 and 4; Table 2). The dashed lines indicate that it is not known whether the observed phenotypes are due to direct or indirect regulation by Fur.