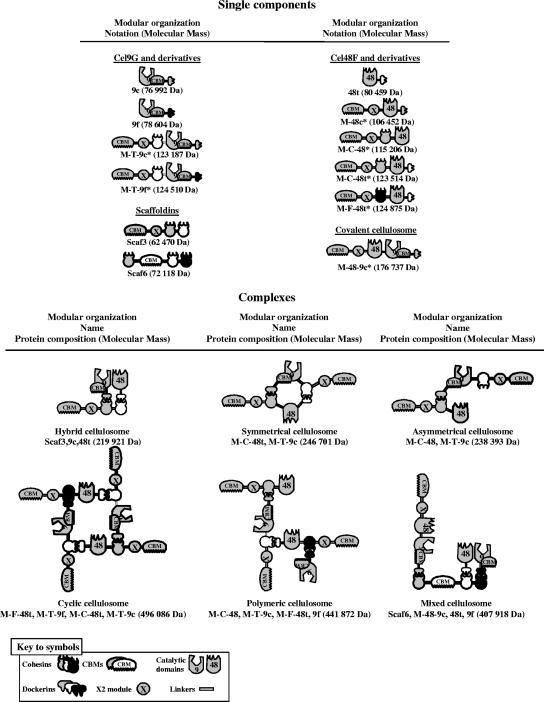
FIG. 1.
Schematic representations of the recombinant proteins and complexes used in this study. The source of the respective module (see the symbol key) is indicated as follows: gray (C. cellulolyticum), white (C. thermocellum), and black (R. flavefaciens). In the shorthand notation for the engineered enzymes, the numbers 9 and 48 refer to the corresponding GH family (GH9 and GH48) of the catalytic module; M designates the tandem CBM3a and X2 modules of the C. cellulolyticum scaffoldin CipC; uppercase letters C, F, and T indicate the source of the cohesin module, C. cellulolyticum, R. flavefaciens, and C. thermocellum, respectively; lowercase letters c, f, and t indicate the source of the dockerin module, C. cellulolyticum, R. flavefaciens, and C. thermocellum, respectively. The names symmetrical, asymmetrical, cyclic, and polymeric are intended both as descriptive terms of the artificial cellulosome-like geometries and to facilitate subsequent narratives in the text. The component compositions are shown schematically and in the shorthand notation are given below the individual elements of the figure. The hybrid and mixed cellulosomes both contain scaffoldins and are thus based on the native complexes. Novel proteins constructed in this study are indicated by an asterisk.