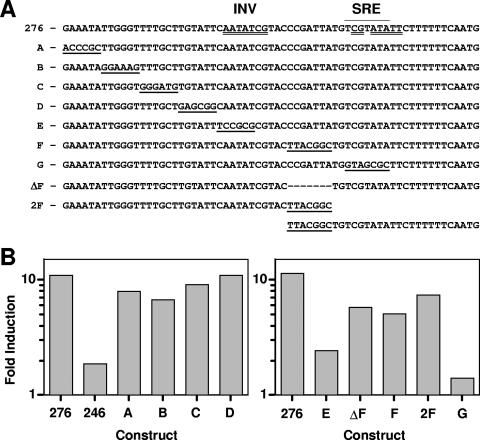
FIG. 5.
Scanning mutations across the azole-inducible region. (A) The region from bp 276 to 212 is shown. An SRE was identified by homology to Saccharomyces and is overlined (region 232-226). A potential inverted repeat sequence at the SRE also was identified (double-underlined sequence spanning region 251-224). The two halves of the inverted repeat include a region coincident with the SRE (region 231-224) and a second, inverted region (INV; region 251-245). Rows A to G indicate constructs with scanning mutations (underlined) not found in the wild-type promoter. ΔF has a deletion of 7 bp (indicated with dashes). 2F has a duplication of 7 bp. To align the sequences, the 2F construct is continued on a second line at the duplication. (B) Promoter constructs were grown in the absence or presence of MICA (10 μg ml−1) for 48 h, and luciferase assays were performed. Induction (n-fold) is expressed as the ratio of luciferase activity in the presence of drug to the luciferase activity in the absence of drug for each construct. These results are from one representative experiment (see Materials and Methods). Left panel, promoter constructs 276 and 246 and linker scan mutations A to D. Right panel, promoter construct 276 and linker scan mutations E, F, and G, and two mutations designed to test spacing. ΔF, deletion of the 7-bp mutation in F; 2F, duplication of the 7-bp mutation in F.