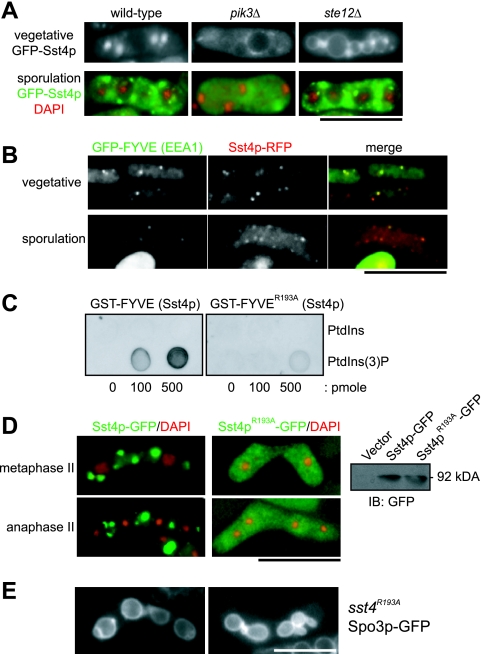
FIG. 5.
Localization and function of Sst4p depend on PtdIns(3)P. (A) Sst4p loses its localization in cells lacking PtdIns(3)P. For this experiment, we used diploid strains because pik3Δ and ste12Δ cells are sterile. Strains TW747 (wild type), TP3 (pik3Δ), and YS2 (ste12Δ) were transformed with the plasmid pREP41(GFP-Sst4p) and incubated as described in the legend for Fig. 4A. (B) Sst4p colocalizes with the FYVE domain of EEA1. Strain MI512 (sst4+-mRFP5) was transformed with plasmid pREP41(GFP-FYVEEEA1) (41) and incubated as described above. The cells were fixed with formaldehyde for 3 min before the pictures were taken. (C) The R193A mutation abolishes the binding of the FYVE domain of Sst4p to PtdIns(3)P. The binding of GST-FYVE and GST-FYVER193A was examined by protein-lipid overlay assay. (D) Sst4pR193A completely loses its specific localization. Strain MI160 (sst4Δ) was transformed with plasmid pAL(Sst4p-GFP) or pAL(Sst4pR193A-GFP). The panel on the right shows proper expression of both proteins confirmed by Western blotting. IB, immunoblot. (E) sst4R193A cells form forespore membranes with bubbles. Sporulation of strain MI597 (sst4R193A) carrying plasmid pAL(Spo3p-GFP) was induced for 14 h. Bars, 10 μm.