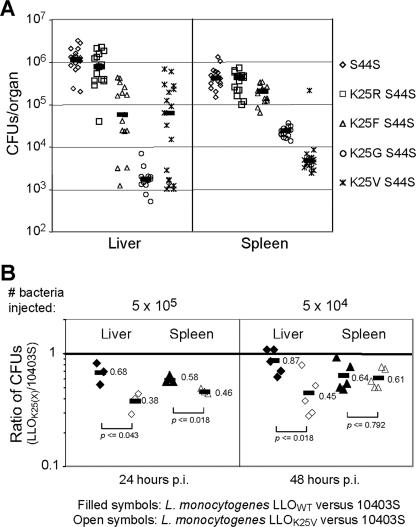
FIG. 7.
Metabolic stabilization of LLO decreases the virulence of L. monocytogenes in mice. (A) BALB/c mice were inoculated, by tail vein injection, with 106 bacteria of the L. monocytogenes strains with the indicated mutations. All bacteria contained the LLO S44S mutation that results in the overproduction of LLO and, in addition, either the wild-type N-terminal Lys residue of LLO or its replacement residue, as shown. CFU were recovered from the livers and spleens 24 h postinoculation by plating dilutions of organ homogenates onto LB plates. Values shown represent the pooled data from at least three independent experiments, with five mice per strain of L. monocytogenes. Black horizontal bars indicate median values for each data set. (B) Competitive indices of L. monocytogenes 10403S versus the complemented hly deletion strains expressing either wild-type LLO or LLOK25V. A 1:1 mixture of complemented Δhly L. monocytogenes and wild-type 10403S L. monocytogenes was coinjected into the tail veins of BALB/c mice. The ratio of each strain in the livers and spleens was determined by plating organ homogenates and subsequently screening 100 colonies for the chloramphenicol resistance phenotype of the complemented strain. The P values indicated were obtained with Student's t test for two samples (http://www.statpages.org).