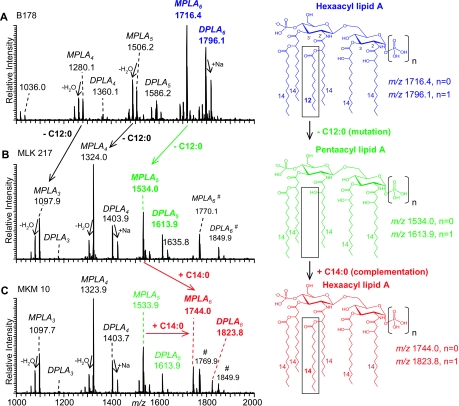
FIG. 2.
Negative-ion vMALDI-LIT mass spectra (using an LTQ LIT) of lipid A. vMALDI-LIT MS of lipid A isolated from (A) E. coli wild-type strain B178, (B) E. coli lpxL mutant strain MLK217 lacking a lauric acid in its structure (dodecanoic acid/C12:0 fatty acid; Δ = −182 Da), and (C) MKM10, an E. coli lpxL strain expressing FTT0232c, which complements MLK217 lipid A with a myristic acid (tetradecanoic acid/C14:0 fatty acid; Δ = +210 Da). Complemented lipid A species were observed with (M-H)− at m/z 1744.0 (MPLA) and 1823.8 (DPLA). Lipid A mass peaks are annotated as DPLA and MPLA, respectively, with their number of fatty acid chains and their assigned composition of fatty acids. (B and C) Two hexa-acyl lipid A species (M-H)− at m/z 1849.9 and 1770.1, marked with a pound sign, are shown that are present only in the lpxL mutant and that contain a palmitoleic acid (C16:1) (also see Fig. S1 in the supplemental material and previous related reports by Karow and Georgopoulis and Sunshine et al. [28, 49]). All spectra yielded monoisotopic masses. The numbers 2′, 3′, 2, and 3 refer to the positions of fatty acid substitutions on the distal (2′ and 3′) and proximal (2 and 3) glucosamine rings of the lipid A core shown in the structure (top right).