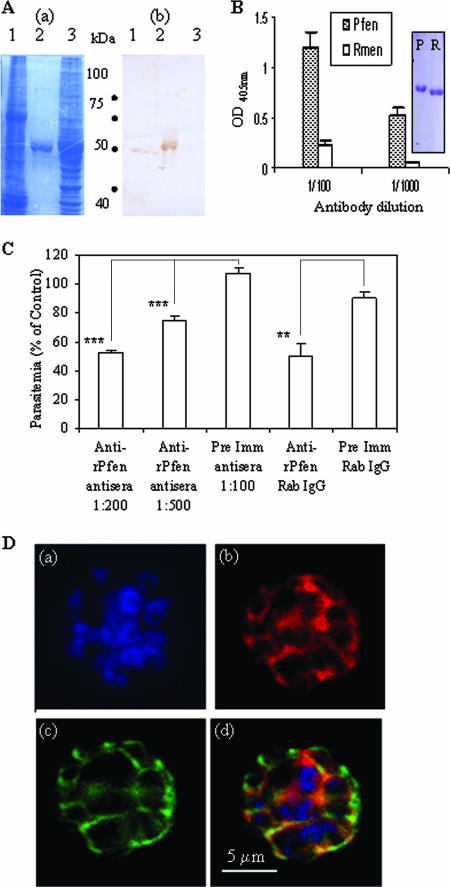
FIG. 2.
(A) SDS-gel electrophoresis of ∼100 μg of cell lysates from P. falciparum and noninfected RBCs (lanes 1 and 3) and ∼5 μg of purified r-Pfen protein (lane 2) was followed by Coomassie blue staining (a) and immunoblotting using rabbit anti-enolase antisera (1:800 dilution) (b). (B) ELISA. Reactivity of equimolar amounts (100 μl of 30 nM solutions) of r-Pfen and RMen, checked with rabbit anti-r-Pfen antiserum at 1:100 and 1:1,000 dilutions. Inset shows the SDS-PAGE analysis and Coomassie blue staining of 10 μl of 30 μM stock solutions of r-Pfen (P) and RMen (R), which were used for the ELISAs. OD, optical density. (C) Effect of polyclonal rabbit antibodies on in vitro growth of synchronized cultures of P. falciparum. Synchronized cultures were treated with rabbit anti-r-Pfen antiserum at dilutions of 1:200 and 1:500 and with rabbit preimmune (Pre Imm) antiserum at a 1:100 dilution. IgG purified from rabbit anti-r-Pfen and preimmune serum was used at a final concentration of 1 mg/ml each. Parasitemia is shown as a percentage of the untreated control. **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001. (D) IFA of the schizont stage of P. falciparum using DAPI (a), rabbit anti-r-Pfen antiserum (1:200) with secondary anti-rabbit IgG conjugated with AlexaFluor 568 (b), and mouse anti-MSP-1 antibodies (1:100) with secondary anti-mouse IgG conjugated with AlexaFluor 488 (c). An overlay of the images from frames a, b, and c is shown in frame d.