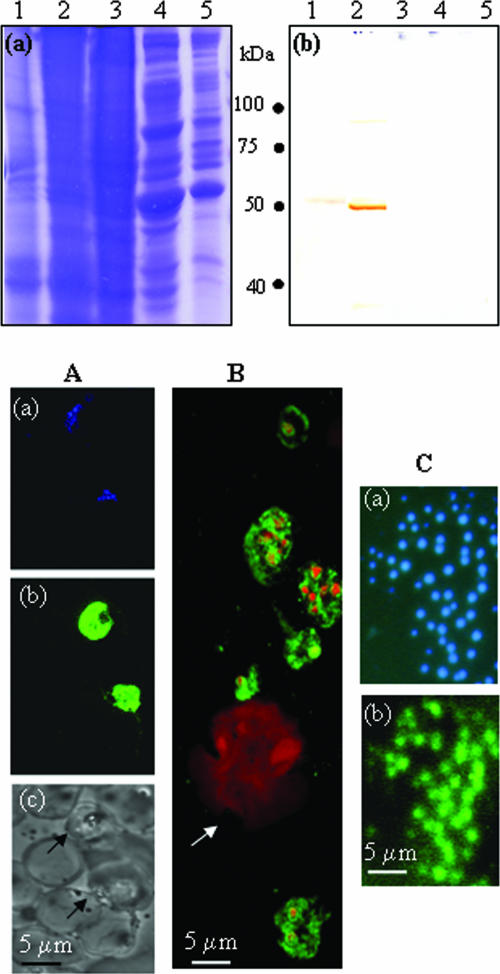
FIG. 4.
(Top panel) Specificity of polyclonal antibodies raised against r-Pfen in mouse: ∼100 μg of proteins from the crude extract of P. yoelii (lane 1), P. falciparum (lane 2), mouse liver (lane 3), human (lane 4), and mouse leukocytes (lane 5) was analyzed on a 12% SDS gel followed by Coomassie blue staining (a) or Western blotting using mouse anti-r-Pfen antisera at 1:800 dilution (b). (Bottom panel) IFA of permeabilized P. falciparum-infected and noninfected human red cells (A), P. yoelii-infected mouse blood smear (B), and nonpermeabilized free P. yoelii merozoites with anti-r-Pfen antiserum (C). Panel A shows the same field of P. falciparum-infected erythrocytes stained with DAPI (blue) (a) and with mouse anti-r-Pfen antiserum (green) (b) and a bright-field image of the area showing infected (arrow) and uninfected erythrocytes (c). (B) Merged confocal image of P. yoelii-infected mouse blood smear stained with DAPI (red) and mouse anti-r-Pfen antiserum (green). The arrow indicates a monocyte. (C) Solution IFA of free P. yoelii merozoites treated with DAPI (a) or rabbit anti-r-Pfen antiserum followed by goat anti-rabbit IgG conjugated with fluorescein isothiocyanate (b). Each antiserum was used at a 1:50 dilution.