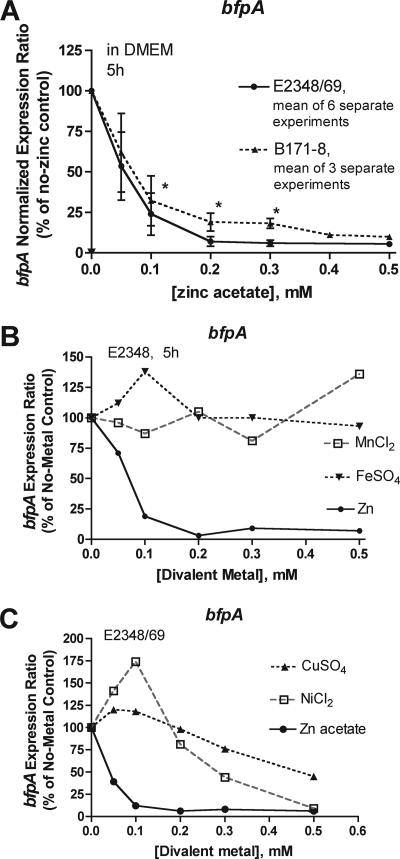
FIG. 2.
Effect of zinc on the expression of BFP as analyzed by reverse transcription and qRT-PCR. Bacteria were lysed with lysozyme, RNA was extracted and subjected to reverse transcription, and then the cDNA was diluted 1,000-fold. Real-time PCR was done in triplicate wells using oligonucleotide primers and monitored by fluorescence from SYBR green dye as described in Materials and Methods. Unknown gene expression was normalized relative to that of rrsB (16S rRNA). The normalized expression ratio was calculated using the 2(−ΔΔCT) method, and then the ratio was multiplied by 100 to express it as a percentage of the no-zinc control. The growth period of strains was 5 h. (A) Effect of zinc on the expression of bfpA in two EPEC strains. Results are means ± standard deviations for 6 and 3 separate experiments, respectively. Symbols: *, statistically significant inhibition compared to the no-zinc condition by analysis of variance with Tukey-Kramer posttest for multiple comparisons. (B and C) Effects of other divalent metals on the expression of bfpA. CuSO4 and NiCl2 inhibited bacterial growth at concentrations above 0.2 mM, but this is taken into account by the normalization method used.