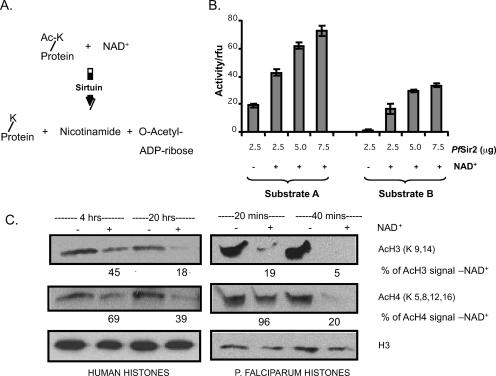
FIG. 3.
Recombinant PfSir2 has NAD+-dependent lysine deacetylase activity. (A) Reaction scheme for NAD+-dependent deacetylase enzymes. (B) Two independent in vitro deacetylase assays were carried out on increasing amounts of PfSir2, with or without 500 μM NAD+. Substrate A is a synthetic AcLys derivative termed ZMAL, and substrate B is a 19-residue synthetic peptide bearing a single AcLys. Assays were carried out in triplicate at 37°C for 16 h, and deacetylase activity is represented in relative fluorescence units (rfu). Error bars indicate standard deviations.(C) Western blots showing histones from sodium butyrate-treated HeLa cells or P. falciparum trophozoites, incubated with recombinant PfSir2 in the presence (+) or absence (−) of 500 μM NAD+ for the indicated times and then probed with antibodies against AcH3, AcH4, or the C-terminal portion of H3 (i.e., total H3). Ratios of acetylated histone signal in the NAD+ (+) reaction to that in the NAD+ (−) reaction are indicated at each time point. Each ratio is normalized to the ratio of total H3 signals in NAD+ and NAD+ lanes.