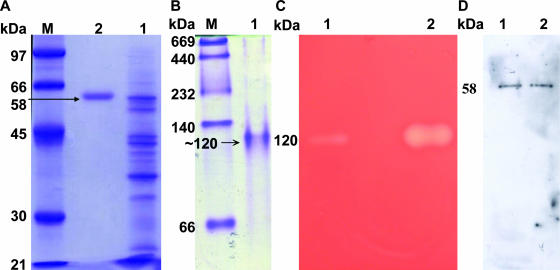
FIG. 1.
Purification and characterization of the hemolytic activity of the Hly-OppA protein from V. furnissii. (A) The extracellular medium from a V. furnissii culture (lane 1) was passed through Phenyl Sepharose 6 Fast Flow, Mono Q, and antibody-conjugated Sepharose 4B columns to obtain a homogeneous protein (lane 2) with a molecular mass of ∼58 kDa, as shown by sodium dodecyl sulfate-PAGE. (B) Native PAGE of purified Hly-OppA, showing a molecular mass of ∼120 kDa. (C) Hemolytic activity detected when the ammonium sulfate-precipitated protein fraction (lane 1) and antibody-conjugated purified Hly-OppA (lane 2) from native PAGE were embedded in a blood agar plate. (D) Immunoblot analysis with antiserum against Hly-OppA, revealing that both the crude (lane 1) and purified (lane 2) proteins yielded a single band. Lane M contained markers.