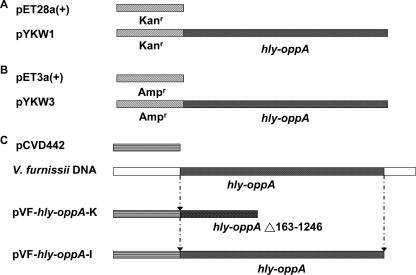
FIG. 3.
Vector construction for expression and knockout of the hly-oppA gene. (A) The full-length hly-oppA gene was treated with the NdeI and EcoRI restriction enzymes and inserted into a kanamycin-resistant pET28a(+) vector predigested with the same enzymes to generate pYKW1. (B) The same hly-oppA open reading frame was inserted into the NdeI/EcoRI sites of ampicillin-resistant pET3a(+) to generate pYKW3. (C) V. furnissii chromosomal DNA was used as a template for amplification of 162 bp of the 5′ end and 305 bp of the 3′ end of the hly-oppA gene. The 467-bp PCR fragment was cloned into an allelic exchange suicide vector, pCVD442, to generate the knockout plasmid pVF-hly-oppA-K. The pVF-hly-oppA-K plasmid was transferred from E. coli to V. furnissii to generate the V. furnissii hly-oppA knockout strain VFYKW1. The full-length hly-oppA gene was cloned into pCVD442 to generate pVF-hly-oppA-I and transferred to VFYKW1 to generate the V. furnissii VFYKW2 strain with hly-oppA restored.