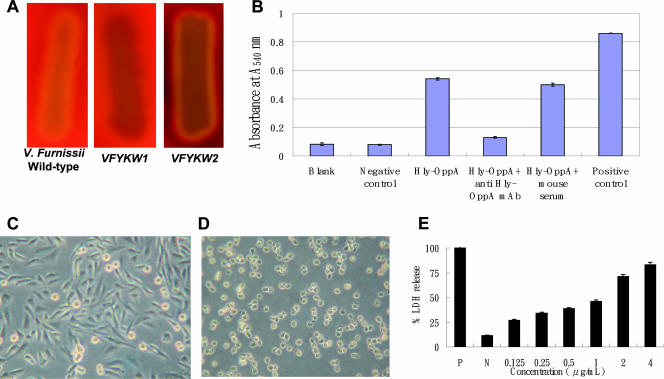
FIG. 5.
Effect of the Hly-OppA protein on the V. furnissii hemolytic phenotype, erythrocyte lysis, morphology, and cytotoxicity in CHO-K1 cells. (A) Hemolytic phenotype of wild-type V. furnissii, VFYKW1, and VFYKW2 on TSA containing 5% sheep blood. (B) Erythrocyte lysis and hemoglobin release caused by purified Hly-OppA protein in the presence or absence of anti-Hly-OppA monoclonal antibody, as measured by the change in absorbance at 540 nm. Blank, PBS buffer; Negative control, BSA (0.5 μg/μl); Hly-OppA, 0.1 μg/μl Hly-OppA; Hly-OppA + anti Hly-OppA mAb, 0.1 μg/μl Hly-OppA plus 0.1 μg/μl anti-Hly-OppA monoclonal antibody; Hly-OppA + mouse serum, 0.1 μg/μl Hly-OppA plus 0.1 g/μl mouse serum; Positive control, 0.1% Triton X-100. (C and D) CHO-K1 cells were not exposed (C) or exposed (D) to the Hly-OppA protein (1 μg/ml) for 30 min at 37°C. (E) Dose-dependent cytotoxicity of the Hly-OppA protein in CHO-K1 cells. CHO-K1 cells were exposed to various concentrations of the Hly-OppA protein for 30 min, and the viability of the cells was determined using a commercial cytotoxicity assay kit. The data are the means and standard deviations from at least three independent experiments.