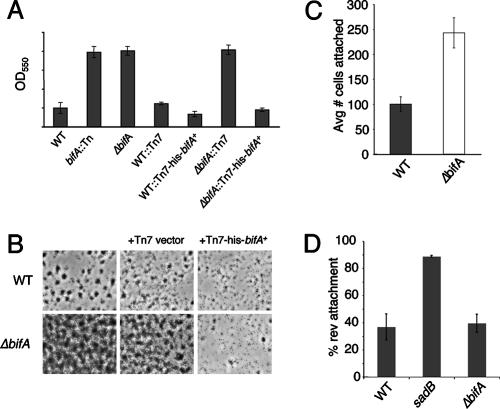
FIG. 1.
Biofilm phenotypes of bifA mutants. (A) Quantification of biofilms formed by the WT, the bifA::Tn mutant and the ΔbifA mutant in the 96-well microtiter dish assay. Also shown are the single-copy complemented strains of the WT and the ΔbifA mutant carrying an insertion of either the Tn7 element alone (WT::Tn7 and ΔbifA::Tn7) or the Tn7 harboring a His-tagged version of bifA (WT::Tn7-His-bifA+ and ΔbifA::Tn7-His-bifA+). Cells were grown in M63 with glucose, MgSO4, and CAA for 6 h at 37°C prior to crystal violet staining. Crystal violet was solubilized in 30% glacial acetic acid and measured at OD550. (B) ALI assay. Top-down phase-contrast images of the WT and the ΔbifA mutant either alone or carrying insertions of the Tn7 (Tn7 vector) or the Tn7 with His-tagged bifA (Tn7-His-bifA+) are shown. Cells were grown in a 24-well plate for 6 h at 37°C, and images were recorded at a magnification of ×1,400. (C) Quantification of initial attachment of the WT and the ΔbifA mutant. Cells were incubated at 37°C for 30 min. Images were recorded at a magnification of ×1,400 over eight fields of view for each strain. The graph indicates the average number of cells attached to the substratum (n = 8) for each strain. (D) Quantification of reversible attachment of the WT, the sadB mutant and the ΔbifA mutant. Strains were incubated in 24-well plates for 5 min at 37°C. Time-lapse images were captured in 1-min intervals and converted to QuickTime movies for analysis. Irreversibly attached cells were scored as cells that did not move during the 1-min interval and were attached by the long axis of the cell. Reversibly attached cells were those that moved during the interval and were attached by a cell pole.