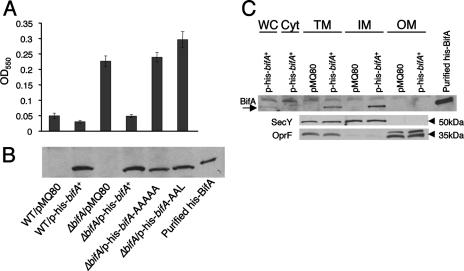
FIG. 4.
Assessment of function, stability, and cellular localization of BifA. (A) Assessment of the ability of the bifA gene, the bifA-AAAAA (GGDEF→AAAAA) mutant, and the bifA-AAL (EAL→AAL) mutant to complement the ΔbifA mutant when provided on an arabinose-inducible plasmid (pMQ80). The graph shows the quantification of biofilm formed by the WT and the ΔbifA mutant carrying either the pMQ80 vector alone or pMQ80 containing the His-tagged bifA gene (p-his-bifA+). Also shown is the quantification of biofilm formed by the ΔbifA mutant carrying pMQ80 with the bifA-AAAAA mutant (p-his-bifA-AAAAA) or the bifA-AAL mutant (p-his-bifA-AAL). Cells were grown for 6 h in the presence of 0.5% arabinose prior to CV staining. (B) Evaluation of expression and stability of WT BifA, BifA-AAAAA, and BifA-AAL proteins expressed from the pMQ80 constructs in panel A. Western blot showing the level of BifA expressed under the same conditions used in the biofilm assays in panel A. Equal amounts of cells were lysed and separated by SDS-PAGE. BifA was detected by using an anti-penta-His antibody. Purified His-BifA served as a control. (C) Cellular localization of BifA. Cellular fractions of the ΔbifA mutant carrying either vector alone (pMQ80) or vector containing the bifA gene (p-his-bifA+) were generated as described previously (see Materials and Methods). Approximately 1 μg of total protein from each fraction was separated by SDS-PAGE. Fractions are indicated as whole-cell (WC), soluble cytoplasmic (Cyt), total membrane (TM), inner-membrane (IM), and outer-membrane (OM) fractions. Western analysis was performed with either an anti-penta-His antibody, an anti-SecY antibody, or an anti-OprF antibody. The arrow indicates the BifA band. Purified His-BifA served as a control. SecY (∼50 kDa) served as a control for inner- membrane localization and OprF (∼35 kDa) served as an outer-membrane marker.