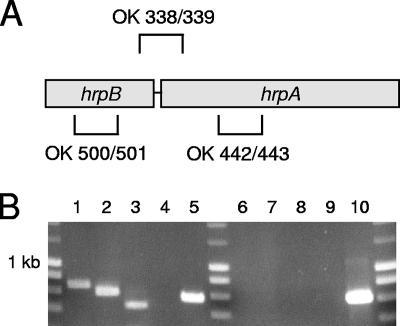
FIG. 3.
RT-PCR analysis of hrpA and hrpB expression in strain 2120. (A) Schematic representation of the primer pairs used in panel B, primers OK338/OK339 (OK 338/339), OK500/OK501 (OK 500/501), and OK442/OK443 (OK 442/443). (B) Transcripts of hrpA and hrpB were detected in total RNA preparations of strain 2120. Additionally, it could be shown that both genes are transcribed into a single mRNA. The following templates were included in the samples: total RNA of strain 2120 (lanes 1 to 3, 5, and 6 to 8), no template (negative control) (lanes 4 and 9), and genomic DNA of strain 2120 (positive control) (lane 10). The primer sets included in the samples were as follows: hrpB-specific primers (OK500/OK501 primers [see panel A]) (lanes 1 and 6), hrpA-specific primers (OK442/OK443 primers [see panel A]) (lanes 2, 7, and 10), primer pair with the forward primer recognizing the 3′ end of the hrpB gene and the reverse primer recognizing a conserved region within the 5′ end of the adjacent hrpA (OK338/OK339 [see panel A]) (lanes 3 and 8), and primers specific for lgtA (OK487/OK488, positive control) (lanes 4, 5, 8, and 9). The samples loaded in lanes 6 to 10 were not subjected to the reverse transcription step of the RT-PCR procedure and served as controls to rule out DNA contamination of the RNA templates.