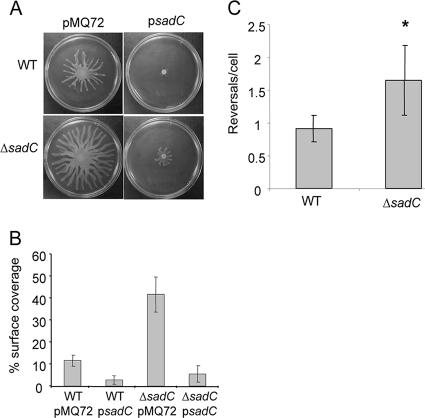
FIG. 2.
The ΔsadC mutant displays hypermotility phenotypes. (A) Swarming motility assays on 0.5% agar plates. Overnight cultures of the WT or ΔsadC strains carrying a vector control (pMQ72) or a sadC-containing plasmid (psadC) were spotted onto swarm agar and incubated at 37°C for 16 h. (B) Average percentage of the plate surface occupied by the respective swarms. Replicate swarm plates (n = 5) for each test strain were grown under identical conditions and then photographed for calculation of the surface area coverage. Averages for the WT (WT/pMQ72) and ΔsadC (ΔsadC/pMQ72) strains carrying vector controls differ significantly (P = 0.001). In both cases, addition of a multicopy sadC-containing plasmid (WT/psadC, ΔsadC/psadC) results in a significant decrease in respective swarm coverage at this time point (P = 0.0088, P = 0.0004). (C) Swim reversals in 15% Ficoll-containing medium quantified from six separate fields of view. The ΔsadC mutant cells on average are observed to reverse more frequently than the parental strain (*, P = 0.01).