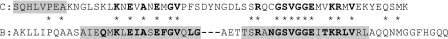FIG. 4.
Comparison of the amino acid sequence of Ssp2 (C) with that of a B. subtilis-derived α/β-type SASP, SspCΔ11-D13K-C3 (B), whose DNA-bound structure is being determined (1). The N-terminal methionine is not shown, since it is removed posttranslationally from α/β-type SASP (13). In line C, the shading highlights the eight amino acids determined by sequence analysis of this protein expressed in B. subtilis spores, and the boldface residues are conserved in ≥95% of all known B. subtilis α/β-type SASP (14). In line B, the shading highlights the two most highly conserved regions in these proteins from Bacillus species, and the boldface residues are identical in ≥95% of all known α/β-type SASP from Bacillus species (14). The asterisks indicate residues that are identical in both proteins.