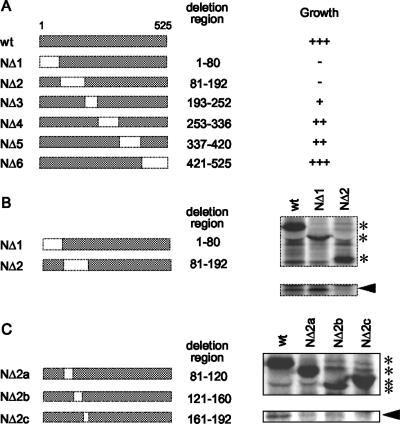
FIG. 3.
Mapping the eIF3-p40-interacting domain of MV-N. (A) Parts of the N gene corresponding to amino acid residues 1 to 80, 81 to 192, 193 to 252, 253 to 336, 337 to 420, and 421 to 525 were deleted, and the resulting deletion clones were inserted into a BD vector for yeast two-hybrid analysis. These constructs were cotransformed with the AD-eIF3-p40 vector into yeast and plated onto selection medium lacking Leu and Trp (SD/−Leu/−Trp). The colonies obtained were spotted on SD/−His/−Leu/−Trp/3-AT plates and incubated at 30°C for 4 days. The apparent binding strength was assessed by the degree of growth and is scored as strong (+++), intermediate (++), weak (+), or absent (−). (B) Myc-tagged MV-N and its deletion clones, NΔ1 and NΔ2, were coexpressed with eIF3-p40 in Cos-7 cells and coimmunoprecipitated using anti-myc antibody. Asterisks indicate immunoprecipitated MV-N or its deletions. An arrowhead indicates the band of eIF3-p40 that was coprecipitated. (C) Parts of the NΔ2 deletion region corresponding to amino acid residues 81 to 120, 121 to 160, and 161 to 192 were further deleted, and the resulting deletion clones were coexpressed with eIF3-p40 in Cos-7 cells and coimmunoprecipitated. The asterisks indicate MV-N or its deletion clones precipitated using anti-myc antibody. Arrowhead indicates the band of eIF3-p40 coprecipitated.