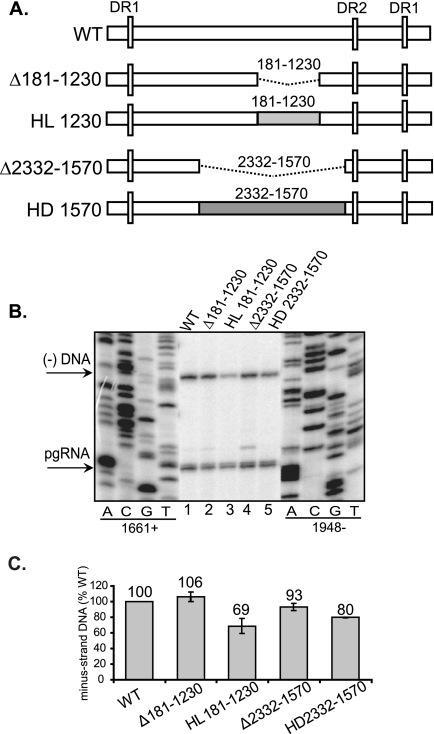
FIG. 3.
Large deletions and heterologous substitutions of the pgRNA are tolerated during the synthesis of minus-strand DNA. (A) WT HBV and HBV/LacZ (HL) or HBV/DHBV (HD) chimeric variants. The white rectangles represent HBV sequences. The dotted lines represent deletions. The coordinates of the deletions are inclusive. The light and dark gray boxes represent LacZ and DHBV sequences, respectively, that were substituted for HBV sequences. The vertical white rectangles represent the DR sequences. (B) Primer extension analysis of replicative intermediates of WT and deletion and substitution variants harvested from cytoplasmic capsids from Huh7 cells. Oligonucleotides 1661+ and 1948− were used to measure minus-strand DNA and pgRNA, respectively. The 5′ ends of minus-strand DNA and pgRNA are indicated on the left. (C) Proportions of minus-strand DNA relative to the WT reference. The level of synthesis of minus-strand DNA is defined as the amount of minus-strand DNA divided by the sum of pgRNA and minus-strand DNA. The values for all variants are normalized to the WT reference. The mean values are from at least six independent transfections of each variant. The error bars indicate standard deviations.