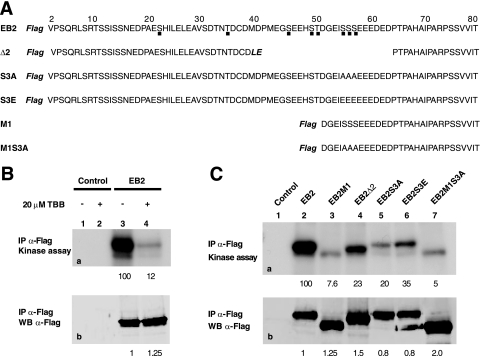
FIG. 6.
EB2 immunoprecipitates contains catalytically active CK2. (A) Amino acid sequences of the EB2 N-terminal 80 amino acids and of EB2 mutants Δ2, S3A, S3E, M1, and M1S3A. The Flag tag is in bold and italics. Amino acids added during the cloning procedure in Δ2 are in bold and italics. Putative CK2 sites are shown by a dot under the EB2 sequence. (B) Extracts from HEK293T cells, mock transfected or expressing F.EB2, were incubated with the M2 anti-Flag affinity gel. Immune complexes were submitted to an in vitro kinase assay in the absence (lanes 1 and 3) or presence (lanes 2 and 4) of the CK2-specific inhibitor TBB (20 μM). Proteins in the immune complexes were resolved by SDS-PAGE and visualized by Western blotting (b) or autoradiography (a). IP, immunoprecipitation. (C) F.EB2, F.EB2M1, F.EB2Δ2, F.EB2S3A, F.EB2S3E, and F.EB2M1S3A expressed in HEK293T cells were analyzed as for panel B. In panels B and C, the relative amounts of EB2 immunoprecipitated were quantified using the Odyssey infrared imaging system. The relative intensities of the radioactive bands on the membrane were quantified using a PhosphorImager. The numbers under blots a correspond to the intensities of the radioactive bands (expressed in arbitrary units compared to EB2) normalized against the amounts of proteins immunoprecipitated (expressed in arbitrary units by comparison to EB2, shown by the numbers under blots b).