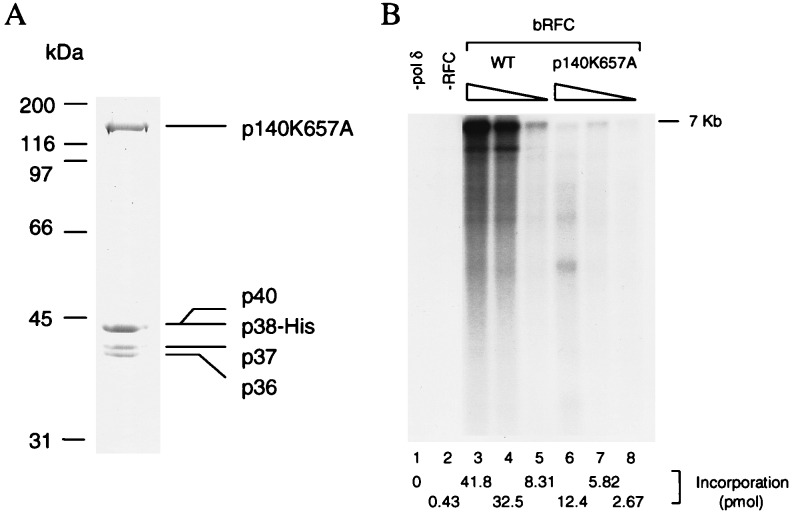
Figure 4.
(A) Purification of hRFCp140K657A. Mutant hRFC was purified from baculovirus-infected high five insect cells cells as described in the Materials and Methods. The purified product (2 μg) was separated by SDS/9% polyacrylamide gels followed by Coomasie staining. (B) Replication activity of mutant hRFC. The wt and mutant hRFCs were examined for their ability to support DNA synthesis from singly primed M13 DNA as described in Materials and Methods. Lanes 1 and 2 represent reactions carried out in the absence of pol δ or RFC, respectively. Wild-type baculovirus RFC was added to the reactions in amount as follows: lane 3, 70 fmol; lane 4, 14 fmol; lane 5, 1.4 fmol. Mutant baculovirus RFC was added to the reactions in amounts as follows: lane 6, 333 fmol; lane 7, 67 fmol; lane 8, 23 fmol. Total nucleotide incorporation (pmol), detected after acid precipitation and liquid scintillation counting, is shown at the bottom of the figure.