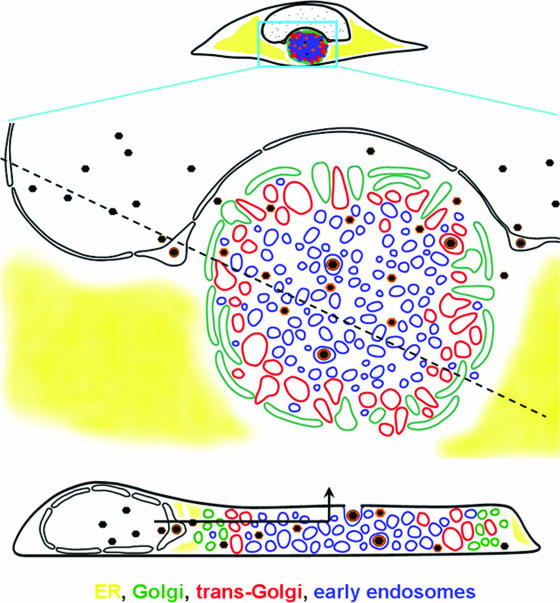
FIG. 6.
Schematic representation of AC structure and the maturational path of nascent virions. The diagram is based on data such as shown in Fig. 1, 3, and 5, coupled with prior ultrastructural analyses (see, for example, reference 50) and other information cited in the text about herpesvirus maturation. In this representation, the AC is the large circular structure that is bounded by Golgi vesicles. The concentric arrangement of the Golgi, TGN, and early endosomal compartments is shown. The cross-sectional representation through the cell at the bottom of the figure shows the nested cylindrical arrangement of the vesicular compartments (sectioning along the dotted line in the upper panel). In this model, nascent capsids acquire a subset of tegument proteins prior to nuclear egress. In the cytoplasm, tegumentation occurs during migration from the AC periphery to the exit vesicle, which is transported vertically to the cell surface without needing to traverse the secretory pathway in reverse. The path of egress is indicated in the lower panel by the arrow.