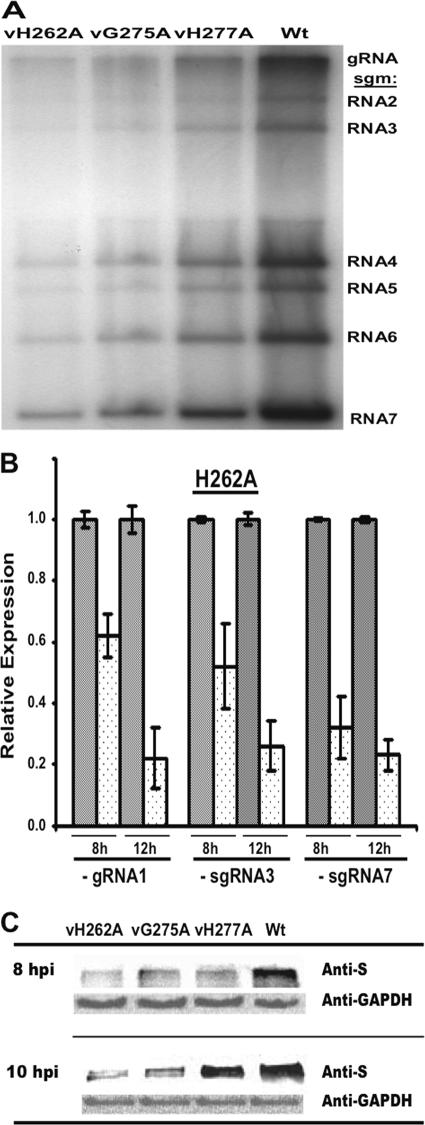
FIG. 4.
Effects of the mutations in mNsp15 on MHV-specific RNA and S protein accumulation. (A) RNA synthesis in cells infected with mNsp15 mutant viruses. Cells were infected with either an mNsp15 mutant virus or WT virus, and viral RNAs were metabolically labeled as described in Materials and Methods. The labeled viral RNAs were separated by formaldehyde agarose gel electrophoresis and visualized by autoradiography. The positions of bands of gRNA and sgmRNAs 1 through 7 are indicated on the right. (B) Effects of the H262A substitution in mNsp15 on MHV minus-strand RNA accumulation. Levels of minus-strand RNAs produced by vH262A and WT virus were determined by RT-qPCR. The relative levels of minus-strand RNA were determined from the threshold values normalized for GAPDH mRNA expression (endogenous control), and then the WT virus value was defined as 1.0. Error bars, standard errors of the means. The symbol + stands for WT virus. The relative levels of expression of the MHV minus-strand RNAs by vH262A (dotted bars) were compared with the levels of expression by WT virus (shaded bars) (α = 0.05). The values shown represent data from three independent experiments. A melting curve showed that there was a single product in each RT-qPCR, and agarose gel electrophoresis of RT-qPCR products confirmed the single RT-qPCR products (data not shown). (C) Expression of MHV S protein by mNsp15 mutant viruses. DBT cells were seeded in a T25 flask, incubated for 24 h, and infected with an mNsp15 mutant or WT virus at an MOI of 1. Total proteins were extracted from the DBT cells at 8 and 10 hpi and were then analyzed in order to detect S protein synthesized by mNsp15 mutant viruses and WT virus by using with a goat polyclonal antibody against MHV S protein (31). As a control, expression levels of GAPDH in DBT cells were determined using mouse anti-mouse GAPDH antibodies and HRP-conjugated anti-mouse IgG antibodies.