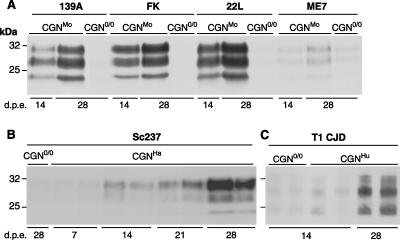
FIG. 2.
Accumulation of PrPres in CGN cultures upon exposure to rodent and human prions. CGN cultures were established from transgenic mice expressing mouse (A), hamster (B) or human (C) PrP and were exposed to brain homogenates (A and B) or purified PrPSc (C) from terminally ill mice infected with prions. CGN cultures established from PrP0/0 transgenic mice (CGN0/0) were also exposed to infectious prions in parallel. (A) CGNMo cultures exposed to mouse strain 139A, Fukuoka-1 (FK), 22L, or ME7 at a final concentration of 0.1% (wt/vol). (B) CGNHa cultures exposed to hamster strain Sc237 at a final concentration of 0.002%. (C) CGNHu cultures exposed to type 1 CJD (T1 CJD) at a final concentration equivalent to 0.1% of brain homogenate. The data shown in panels B and C correspond to duplicate culture wells within a representative experiment. In all PrP-expressing cultures, PrPres accumulation increased from 14 to 28 days postexposure (d.p.e.) and was weak or absent in nonpermissive CGN0/0 cultures. Cell lysates were PK treated, and PrPres was detected by immunoblotting using biotinylated monoclonal antibody ICSM18 (A and C) or Sha31 (B).