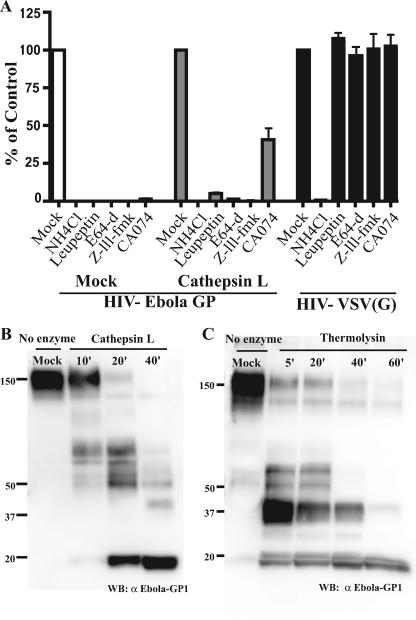
FIG. 1.
Proteolysis of Ebola virus GP and inhibition of infection using cathepsin inhibitors. (A) VeroE6 cells were treated with NH4Cl (50 mM), leupeptin (10 μM), E64-d (10 μM), Z-LLL-FMK (10 μM), or CA074 (100 μM) for 1 h at 37°C prior to infection with mock- or CatL-treated HIV-Ebola virus GP pseudovirions encoding a luciferase reporter gene. HIV-VSV(G) pseudovirion infection was monitored as a control. Infectivity was quantified 48 h postinfection by measuring luciferase activity in cell lysates. Results are reported as the percent infection of mock-treated cells and are the means and standard deviations for samples run in triplicate. HIV-Ebola virus GP pseudovirions were mock treated or treated with 10 μg/ml of CatL at pH 5.5 with 4 mM DTT (B) or 0.5 mg/ml thermolysin at pH 7.5 (C) for the indicated times. CatL reactions were terminated with 10 μM leupeptin, and thermolysin activity was blocked with the addition of 0.1 mM EDTA. Samples were analyzed on a 4 to 15% sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel and immunoblotted with polyclonal Ebola virus GP1 antisera.