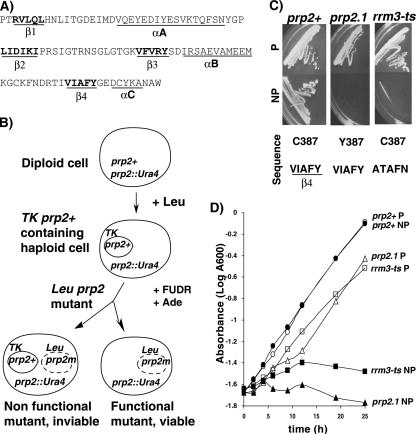
FIG. 5.
Isolation and characterization of temperature-sensitive mutants in RRM3. (A) Amino acid sequence of the RRM3 domain of U2AF59. The β strands (β1 to β4) and α helices (αA to αC) are indicated. Amino acids targeted for mutagenesis are shown in bold. (B) Schematics for the generation and screening of RRM3 mutants. Heterozygous diploid cells used to obtain a haploid U2AF59 genomic knockout strain carrying prp2+ in the TK plasmid were transformed with RRM3 mutant libraries (prp2m). The transformants were screened for viable mutants followed by replica plating for growth at permissive and nonpermissive temperatures as described in Materials and Methods. (C) Characterization of U2AF59 RRM3 ts mutants. The wild-type (prp2+), prp2.1, and rrm3-ts strains were incubated at permissive (P; 25°C) or nonpermissive (NP; 37°C) temperature. Amino acid sequences of the wild type and substitutions in prp2.1 and the RRM3 mutant are shown. (D) Growth curve. The strains shown in panel C were grown in liquid cultures at permissive and nonpermissive temperatures, and the cell density was measured using absorbance at 600 nm at various time intervals.