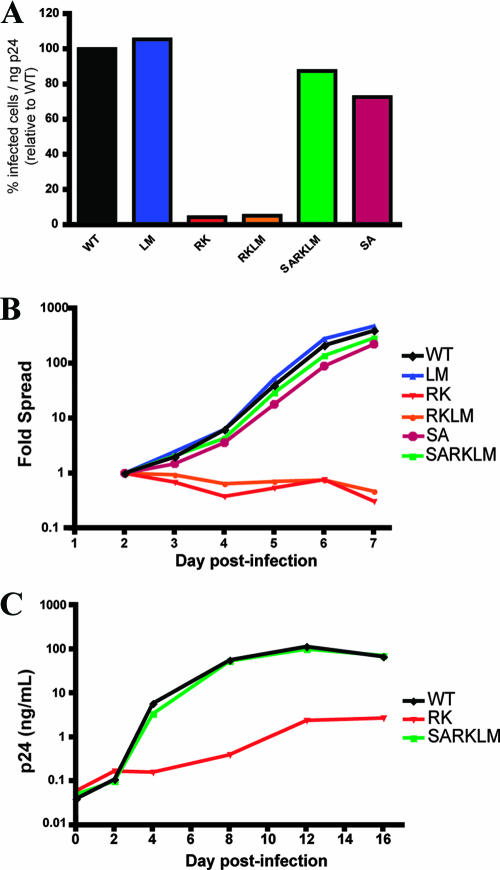
FIG. 2.
Escape mutation R264K substantially impacts viral replication in vitro. (A) CEM-GXR cells were infected with WT or variant viruses (100 μl of viral stocks), and the percentage of infected GFP-positive (GFP+) cells/ng p24 was determined at 48 h by flow cytometry. Values were normalized to WT values (black). The RK (red) and RKLM (orange) variants exhibited substantial deficiencies in infectivity, while only minor differences were observed for LM (blue), SA (purple), and SARKLM (green). Results shown are representative of three or more independent experiments. (B) CEM-GXR cells were infected (multiplicity of infection of 0.0015), and viral spread was measured over 7 days using flow cytometry to quantify GFP+ cells. The percentage of infected cells was normalized to the value at day 2 (0.15%). Again, RK (red) and RKLM (orange) exhibited deficiencies in replication, while SARKLM virus (green) replicated efficiently. Results shown are representative of three independent experiments. (C) The replicative defect of the RK variant was confirmed using primary cells. PBMC were inoculated with virus (10 ng p24), and viral spread was measured by p24 ELISA over 16 days. WT (black) and SARKLM (green) replicated similarly, while the RK variant (red) generated less p24 at all times tested. Results shown are representative of three independent experiments using different donors.