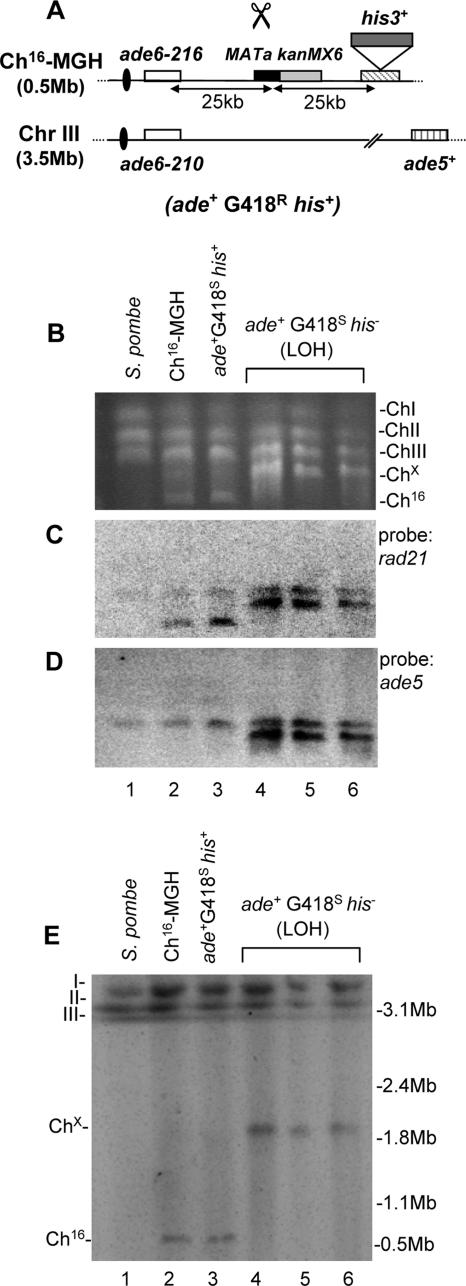
FIG. 1.
DSB-induced LOH results from large translocations in a wild-type background. (A) Schematic of the Ch16-MGH strain. Ch16-MGH, ChIII, centromeric regions (ovals), complementary heteroalleles (ade6-M216 and ade6-M210) (white), ade5+ (vertical stripes), and a MATa site (black) with an adjacent kanMX6 resistance marker (gray) are shown, as previously described (45). The his3+ marker (dark gray) was inserted ∼25 kb downstream of the MATa site. Derepression of pREP81X-HO (not shown) generates a DSB at the MATa target site (scissors). In Ch16-MHH, kanMX6 is replaced by hph. (B) PFGE analysis of chromosomal DNA from a wild-type S. pombe strain (lane 1), an “uncut” wild-type strain (TH1436) encoding Ch16-MGH (Ch16-MGH; lane 2), a strain encoding Ch16-MGH repaired by gene conversion following DSB induction (ade+ G418s his+; lane 3), and three individually isolated ade+ G418s his− colonies following DSB induction (lanes 4, 5, and 6). (C and D) Southern blot analysis of the PFGE shown in panel B probed with rad21 (C) and ade5 (D). (E) High-resolution PFGE analysis of colonies shown in panel B.