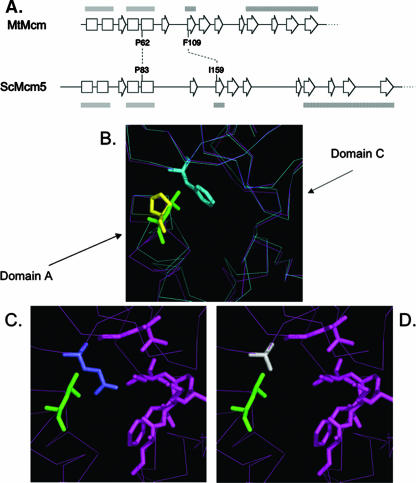
FIG. 1.
Structural models of archaeal M. thermoautotrophicum MCM protein. (A) Diagram depicting the conserved secondary structure of the N terminus of M. thermoautotrophicum (archaeal) Mcm (MtMcm) and of S. cerevisiae Mcm5 (ScMcm5) (13). Boxes, α-helices; block arrows, β-sheets; gray bars, domain A; hatched bars, domain C. (B) Interaction between domains A and C in the archaeal Mcm protein. P62L is depicted in green, and F109 is depicted in light blue. Superimposed in yellow is the modeled position of the yeast P83. Notice the movement of domain A away from domain C when P62L is present (magenta lines) compared to the wild-type conformations (blue lines). (C) Yeast Mcm5 modeled on the basis of the archaeal Mcm protein. P83L is in green, and I159 is in purple. (D) Modeled P83L (green) and I159A (gray) in yeast Mcm5 protein.