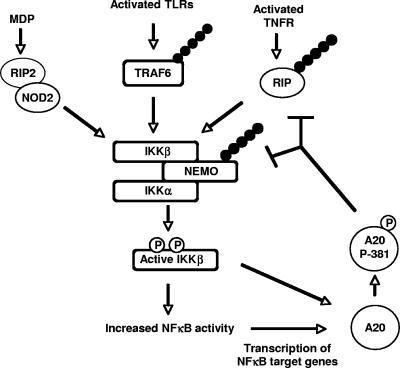
FIG. 7.
Model for the role of A20 phosphorylation at Ser381 in the inhibition of NF-κB responses. Recognition of pathogens or proinflammatory cytokines by cells of the innate immune system leads to activation of IKKβ. Active IKKβ leads to the transcription of NF-κB target genes, including A20. If IKKβ activity remains high following A20 translation, IKKβ phosphorylates this newly translated A20 at serine 381. This phosphorylation increases the activity of A20, allowing it to more forcefully downregulate the NF-κB pathway.