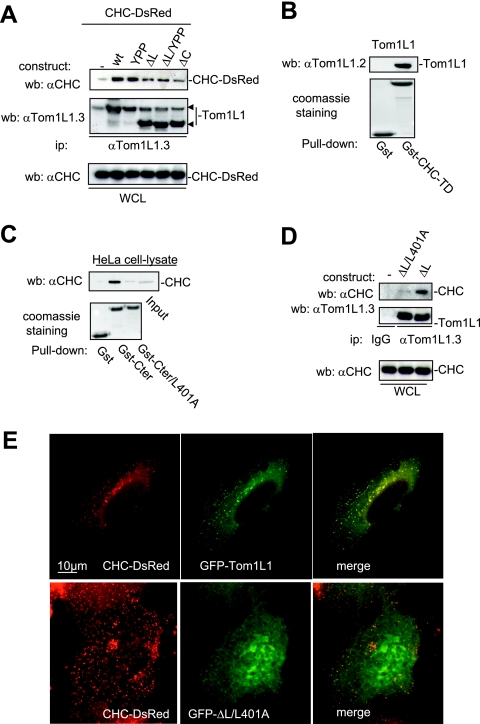
FIG. 2.
CHC-Tom1L1 complex formation. (A) Association of CHC with Tom1L1 involves both the linker and the C-terminus sequences. HEK 293 cells were transfected with CHC-DsRed and the indicated Tom1L1 constructs. Tom1L1 proteins were immunoprecipitated (ip) with the anti-Tom1L1.3 (αTom1L1.3) antibodies, and the presence of associated CHC-DsRed was revealed by Western blotting (wb) with anti-CHC (αCHC) antibodies. The levels of associated CHC-Ds-Red, immunoprecipitated Tom1L1, and expressed CHC-DsRed are shown. wt, wild type; WCL, whole-cell lysate. (B) In vitro association of Tom1L1 with Gst-CHC-TD fusion protein. The indicated fusion protein bound to glutathione beads was incubated with the purified Tom1L1. The presence of Tom1L1 was revealed by Western blotting with the indicated antibody. (C) Association of Tom1L1 C terminus with CHC involves a Leu-rich motif at the C terminus. HeLa cell lysates were incubated with indicated GST fusion proteins or control GST beads, and the interaction with CHC was revealed by Western blotting with a specific antibody. Input (5% of the cell lysates) was included as a positive control. (D) Regulation of CHC-Tom1L1 complex formation by the linker and the Leu-rich motif L401LQPSVL. Tom1L1 was immunoprecipitated from lysates of HEK 293 cells transiently expressing the indicated constructs with the anti-Tom1L1.3 antibodies or a control immunoglobulin G (IgG), and the presence of associated CHC was revealed by Western blotting using anti-CHC antibodies. The levels of expressed and associated CHC and immunoprecipitated Tom1L1 are shown. (E) Colocalization of CHC with Tom1L1. Shown is the representative fluorescence of CHC-DsRed, GFP-Tom1L1 (top panels), or a GFP-Tom1L1 mutant that does not associate with CHC (ΔL/L401A) (bottom panel). Also shown is the merged image of a cotranfected NIH 3T3 cell as obtained after deconvolution (Huygens software).