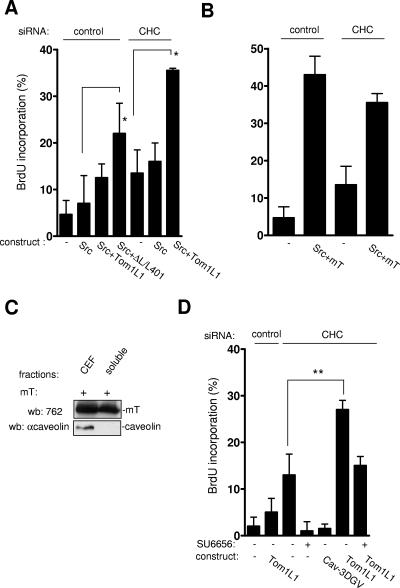
FIG. 8.
Tom1L1 that does not associate with CHC increases Src-driven DNA synthesis. (A) Tom1L1 that does not associate with CHC increases wild-type Src-driven DNA synthesis. NIH 3T3 cells seeded onto coverslips and transfected or not with the indicated Tom1L1 constructs and CHC siRNA, as indicated, were incubated in 0.5% serum for 30 h and further incubated in the presence of BrdU for 18 h. Cells were then fixed and processed for immunofluorescence. (B) CHC does not regulate the capacity of mT antigen to enhance Src-driven DNA synthesis. Shown is BrdU incorporation (mean ± standard deviation [n = 4]) of serum-starved NIH 3T3 cells that were transfected with indicated constructs and the indicated siRNAs as shown. (C) mT antigen is preferentially localized in CEF. Shown are the level of mT antigen in CEF and soluble fractions (fractions 7 to 9 [“soluble”]) from HEK 293 cells expressing mT antigen. The level of caveolin is also shown. wb, Western blotting; αcaveolin, anticaveolin. (D) Tom1L1 enhances DNA synthesis in CHC-depleted NIH 3T3 cells in a Src-dependent manner. NIH 3T3 cells seeded onto coverslips and transfected or not with the indicated constructs and CHC siRNA, as indicated, were incubated in 0.5% serum for 30 h, treated or not with SU6656 (2 μM) as shown, and further incubated in the presence of BrdU for 18 h. Cells were then fixed and processed for immunofluorescence. The percentage of transfected cells that incorporated BrdU was calculated as described in Materials and Methods. The percentage of transfected cells that incorporated BrdU was calculated as described in Materials and Methods. Results are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation of three to four independent experiments. *, P < 0.05, and **, P < 0.01, by Student's t test.