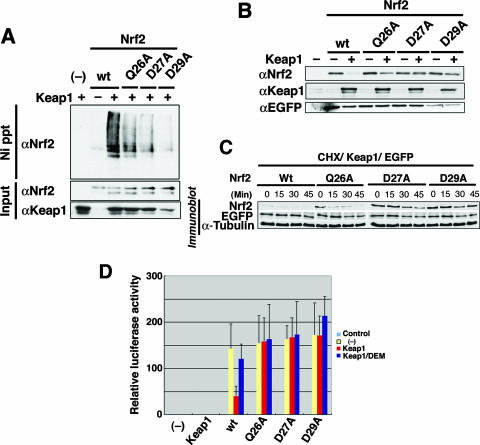
FIG. 4.
The DLG motif facilitates the Keap1-mediated ubiquitination and protein turnover of Nrf2. (A) Keap1-mediated ubiquitination of wild-type (wt) Nrf2 (lanes 2 and 3) and Gln26Ala (Q26A), Asp27Ala (D27A), and Asp29Ala (D29A) mutants of Nrf2 were examined in the absence (−) or presence (+) of Keap1 by an in vivo ubiquitination assay in 293T cells. Lane 1 is a negative control without Nrf2 input (−). Modified Nrf2 was retrieved by nickel beads (Ni precipitation [Ni ppt]) and monitored by anti-Nrf2 antibody (αNrf2). The protein inputs for Nrf2 and Keap1 were detected by immunoblotting using anti-Nrf2 (αNrf2) and anti-Keap1 (αKeap1) antibodies, respectively. (B) The protein stabilities of wild-type Nrf2 (wt) or mutant Nrf2 (Q26A, D27A and D29A) in steady state were evaluated by immunoblotting in the absence (−) or presence (+) of Keap1 (αNrf2). Keap1 protein input in Cos7 cells and transfection efficiency controls using EGFP plasmid (anti-EGFP antibody [αEGFP]) are shown in the middle and bottom blots, respectively. (C) Protein stability of wild-type (Wt) and mutant Nrf2 after cycloheximide (35 μg/ml) treatment was monitored in 293T cells at 0, 15, 30, and 45 min. Transfection efficiency (EGFP) and protein input (α-Tubulin) controls are as shown. (D) The transactivation activities of wild-type and mutant Nrf2 (as indicated under the bar graph) in Cos7 cells were studied using a luciferase reporter assay in the absence (yellow bars) or presence (red and blue bars) of Keap1. Cells were treated with (blue bars) or without (red bars) the phase II enzyme inducer DEM. The leftmost bar (−) is a negative control with vehicle only.