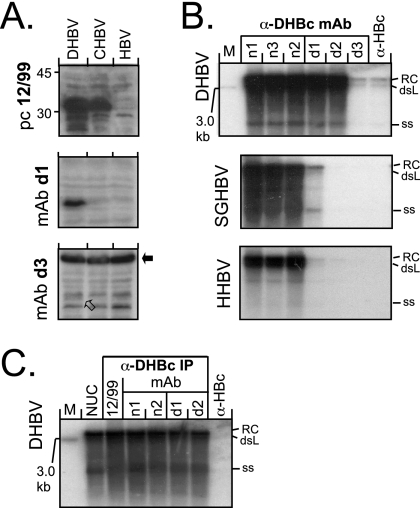
FIG. 4.
Reactivity of anti-DHBc MAbs with denatured avihepadnaviral core proteins and native, authentic nucleocapsids. (A) SDS-WB analysis of crude cytoplasmic lysates. Aliquots (5 μl) of cytoplasmic lysates from transfected LMH cell were directly analyzed by SDS-WB and probed with the different antibodies. As examples, blots of lysates from cells transfected with vectors for DHBV, CHBV, and HBV as a negative control and probed with the indicated antibodies are shown. MAb d3 gave only a weak signal at the DHBc position (open arrow) but strongly cross-reacted with a cellular protein of ∼60 kDa (black arrow). CHBV core protein was detectable by serum 12/99 but by neither MAb. (B) Southern blot of nucleocapsid-borne avihepadnaviral genomes coprecipitated by anti-DHBc MAbs. Viral DNAs isolated from cytoplasmic nucleocapsids immunoprecipitated by the indicated antibodies were detected by using a 32P-labeled DHBV probe. Results similar to those shown for HHBV and SGHBV were obtained with RGHBV, STHBV, and CHBV (see Fig. S2 in the supplemental material). The positions of the relaxed circular (RC), double-stranded linear (dsL), and single-stranded (ss) DNA forms are indicated. M, linear 3.0-kb marker DNA fragment. (C) Anti-DHBc MAbs recognize differently matured DHBV nucleocapsids with similar efficiency. Nucleocapsid-associated viral DNAs from transfected cells were isolated by either by nuclease treatment (1) of cytoplasmic lysates (lane NUC) or by immunoprecipitation with either the polyclonal antiserum 12/99 or the indicated MAbs and then analyzed by Southern blotting as in panel B. No significant differences in the ratios of the different DNA forms were observed.