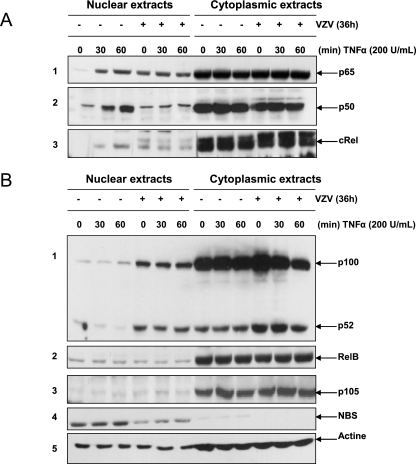
FIG. 5.
Nuclear translocation of NF-κB subunits is disrupted by VZV infection of MeWo cells. MeWo cells were either mock or VZV infected for 36 h prior to treatment with TNF-α (200 U/ml) for increasing times. The nuclear and cytoplasmic levels of various NF-κB subunits, activated mostly via the classical NF-κB activation pathway (p65, p50, and c-Rel) (A) or the alternative pathway (p100, p52, and RelB) (B), were analyzed by Western blotting. Nuclear and cytoplasmic contaminations were evaluated using anti-p105 and anti-NBS antibodies, respectively. Actin was used as a loading control.