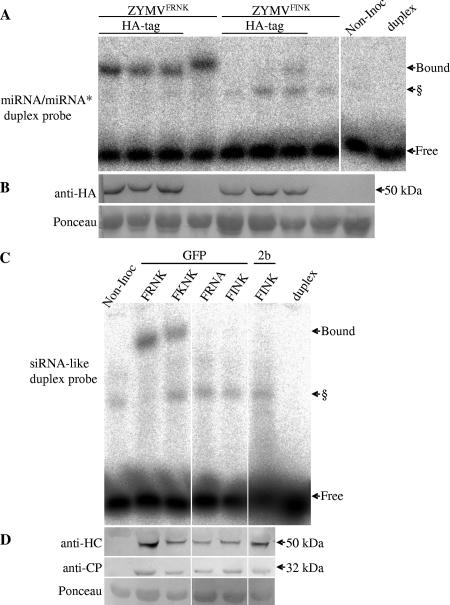
FIG. 4.
The ZYMV HC-Pro FRNK motif is involved in double-stranded smRNA duplex binding. Squash leaf extracts were prepared for EMSA from ZYMV-infected (A and B) or foreign-gene-expressing, ZYMV-infected (C and D) plants. Panel A shows HC-Pro binding to an artificial miRNA/miRNA*-like duplex probe, and panel C shows HC-Pro binding to an artificial siRNA-like duplex probe. The corresponding protein-level controls for each experiment are shown in the Western blots in panels B and D. (A and B) Three leaf samples with HA-tagged HC-Pro-expressing virus and one sample with virus expressing untagged protein were collected at 5 dpi (for either severe ZYMVFRNK- or attenuated ZYMVFINK-infected plants), along with a noninoculated control sample (Non-Inoc.). (C and D) Representative samples from leaves inoculated with ZYMV clones that expressed GFP or CMV Fny 2b (2b) and had the indicated mutations in the FRNK motif. Bound and free radiolabeled duplexes are indicated by arrows. The radiolabeled probe alone was run as a control (duplex). § denotes a putative endogenous plant RNA duplex-binding protein that was sometimes observed in EMSA of infected and noninoculated samples. The miRNA/miRNA* duplex probe was based on the human precursor of miR16 and included mismatches and noncanonical base pairing, and the siRNA-like duplex probe had an artificial fully matching sequence with 3′ overhangs. Western blots were probed with monoclonal anti-HA antibody (B) or polyclonal anti-ZYMV HC-Pro and anti-ZYMV CP antibodies (D). Ponceau staining of the same membrane, as an equal loading control, is shown. The expected sizes of the HC-Pro monomer and the CP are marked by the arrows (50 kDa and 32 kDa, respectively).