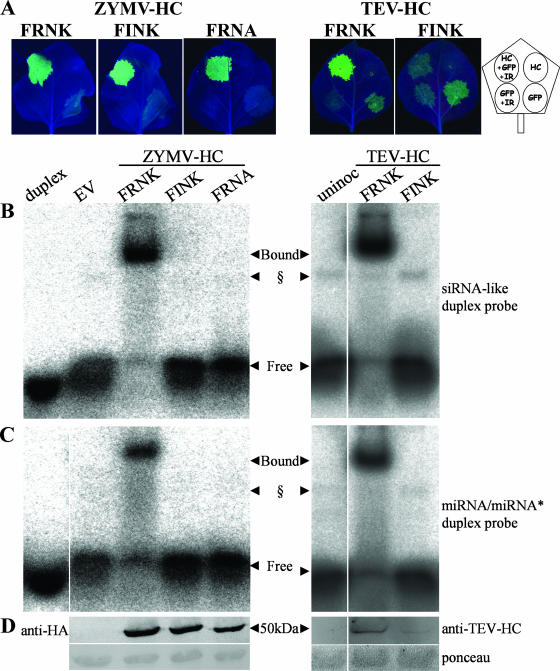
FIG. 6.
Replacement of positively charged amino acids in two different locations of ZYMV HC-Pro reduces duplex RNA binding without abolishing RSS activity. (A) ZYMV HCFINK and ZYMV HCFRNA overexpressed in N. benthamiana are active as suppressors, while TEV HCFINK is inactive. N. benthamiana leaves were agrobacterium infiltrated with different combinations of binary constructs overexpressing the different HC-Pro constructs ZYMV HCFRNK, ZYMV HCFINK, ZYMV HCFRNA, TEV HCFRNK, and TEV HCFINK. ZYMV suppressors were HA tagged. Pictures of detached leaves were taken at 4 dpi (right panel) or 7 dpi (left panel) under UV illumination. The diagram (far right) shows the leaf infiltration pattern with binary constructs (HC-Pro construct [HC], GFP-expressing construct [GFP], GFP-silencing inverted-repeat construct [IR]). All cultures were diluted in each other or in culture with EV to an OD600 of 0.5. (B and C) Binding assay. Leaf extracts from a separate leaf from the same plants as those in panel A were collected at 3 dpi for EMSA, which was conducted with radioactive artificial siRNA (B) or miRNA (C) duplexes. (D) The same extracts were used for Western blot analysis with the antibodies shown. The amounts of HC-Pro protein loaded per lane were estimated to be 1.7 μg for ZYMV HCFRNK and 1.1 μg for ZYMV HCFINK. TEV HCFRNK protein levels were estimated to be 10-fold greater than TEV HCFINK levels. The concentration of each probe used in the binding assays was 5 nM. § marks a putative plant-endogenous duplex-binding protein that is sometimes observed. uninoc, uninoculated.