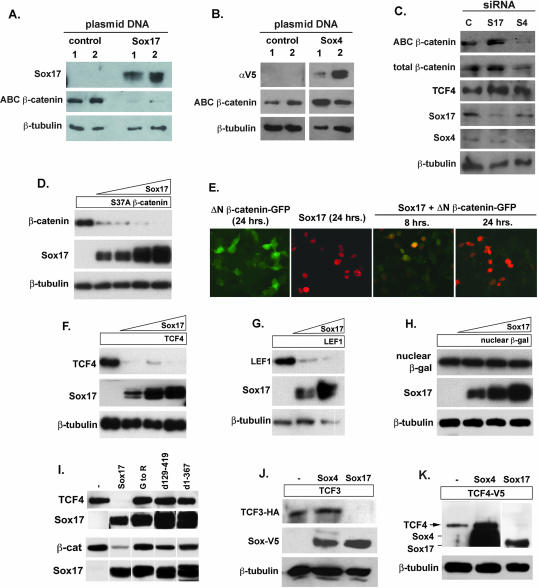
FIG. 7.
Sox proteins affect β-catenin and TCF/LEF protein levels. (A and B) Effects of Sox17 and Sox4 overexpression on endogenous β-catenin protein levels in SW480 cells. The overexpression of Sox17 in SW480 cells causes significant reduction in the levels of endogenous unphosphorylated β-catenin protein, which was detected using an antibody specific for unphosphorylated β-catenin (ABC β-catenin). The overexpression of Sox4 caused an increase in the levels of endogenous unphosphorylated β-catenin protein. αV5, anti-V5 antibody. (C) Impact of siRNA knockdown of Sox17 (S17) and Sox4 (S4) on β-catenin and TCF4 levels in SW480 cells. Reduced levels of endogenous Sox4 protein coincide with a significant decrease in unphosphorylated β-catenin protein. Reduced levels of endogenous Sox17 protein coincide with a slight increase in β-catenin and TCF4 protein levels. C, control. (D) Sox17 promotes the degradation of stabilized β-catenin protein in a dose-dependent manner. COS cells (or 293T cells [data not shown]) were transfected with a plasmid encoding stabilized β-catenin (carrying the S37A mutation and tagged with V5 epitope; 100 ng) alone or with increasing amounts of a Sox17 expression plasmid (50, 100, 200, and 400 ng). After 24 to 48 h, cell lysates were harvested and analyzed by Western blotting using anti-V5 (β-catenin), anti-Sox17, and anti-β-tubulin antibodies. (E) Time course of Sox17-mediated reduction in stabilized β-catenin protein. Cells were transfected with a Sox17 plasmid (100 ng) and a plasmid encoding stabilized, GFP-tagged β-catenin (ΔN β-catenin-GFP; 100 ng) alone or together. The expression levels of Sox17 and β-catenin were analyzed 8 and 24 h posttransfection by the analysis of GFP for β-catenin or by immunohistochemistry analysis with a Sox17 antibody. (F and G) Sox17 promotes the degradation of TCF4 (F) and LEF1 (G) proteins in a dose-dependent manner. (H) A Sox17 plasmid (50, 100, and 200 ng) had no effect on the levels of expression of nuclear β-galactosidase protein (β-gal), demonstrating that Sox17 did not generally affect the transcription or translation of plasmids in cotransfected cells. β-tubulin protein was used to indicate that each lane contained roughly equivalent amounts of total protein. (I) The interaction of Sox17 with either TCF4 or β-catenin (β-cat) is required for the degradation of these proteins. COS cells were cotransfected with plasmids encoding Sox17 mutant forms and TCF4 or β-catenin, and degradation was analyzed by Western blotting of cell extracts after 48 h. The relative levels of expression of the V5 epitope-tagged Sox17 mutant forms are shown in the bottom panel. Mutant forms of Sox17 that retained the ability to interact with TCF but failed to interact with β-catenin were unable to promote TCF4 degradation and vice versa, suggesting that interaction with both is required for degradation. −, control. (J and K) Effects of Sox4 versus Sox17 on TCF3 and TCF4 protein levels. Sox4, Sox17, and TCF4 proteins were detected by Western blotting with an anti-V5 antibody and closely comigrate, as indicated in panel K. TCF3 protein was detected using a HA epitope tag, and the Sox proteins were detected using a V5 epitope tag. β-Tubulin protein was used to indicate that each lane contained roughly equivalent amounts of total protein. −, control. For all panels, experiments were repeated at least three times and results from a representative experiment are shown.