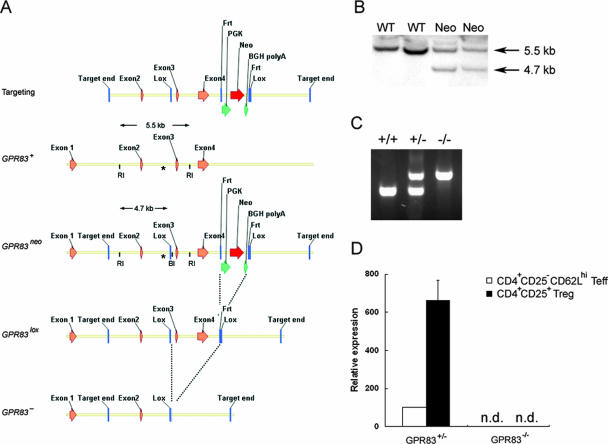
FIG. 1.
Generation of GPR83-deficient mice. (A) Schematic representation of the targeting construct used to generate mice harboring a GPR83 knockout allele. Two loxP sites were introduced, one prior to exon 3 and one after exon 4, as described in Materials and Methods. Chimeric males were mated first to FLP deleter mice to excise the neomycin resistance gene (neo) and next to Cre deleter mice to generate the GPR83 null allele. BGH, bovine growth hormone; RI, EcoRI; BI, XbaI. (B) Southern blot analysis was performed to screen positive ES clones for evidence of homologous recombination. Genomic DNA was digested with EcoRI and XbaI and hybridized with the probe depicted (labeled with an asterisk) in the panel. (C) PCR screening of Gpr83-targeted allele transmission. Breeding was set up by using a heterozygous male crossed with homozygous mutant females. (D) The expression of GPR83 mRNA in purified CD4+ CD25− CD62Lhi T cells (naïve effector T cells [Teff]) and CD4+ CD25+ CD62Lhi T cells (Treg cells) from GPR83−/− mice and control GPR83+/− littermates was measured by real-time RT-PCR (n.d., none detectable).