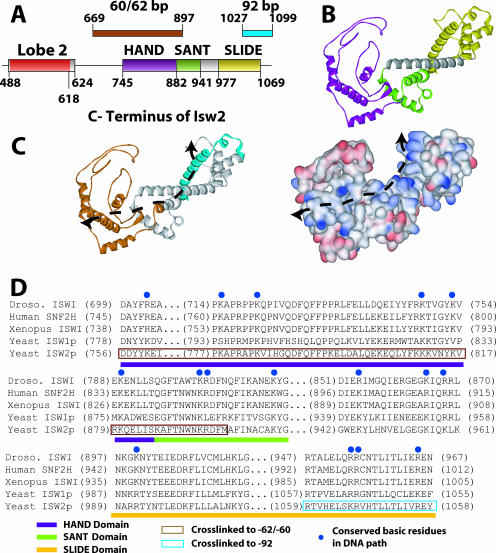
FIG. 6.
Model for the C terminus of Isw2 and its interaction with the nucleosome. (A) The positions of the HAND, SANT, and SLIDE domains in Isw2 are shown and correlated with the regions of Isw2 that were cross-linked to nucleosomal and extranucleosomal DNA 60 to 62 and 92 bp from the dyad axis. (B) A model of a portion of the C terminus of Isw2 is shown, with the HAND domain in purple, the SANT domain in light green, the SLIDE domain in yellow, and the spacer helix in gray. (C) A DNA binding path is suggested by the surface charge distribution of the Isw2 C-terminal domain model and the regions found to be cross-linked to DNA. The same model that is shown in panel B is depicted with the regions cross-linked to the entry/exit site in brown and extranucleosomal DNA in cyan (left panel). The distribution of the surface charges (positive in blue, negative in red) of the Isw2 C-terminal domain model suggests a putative path of DNA as indicated by the dashed line (right panel). (D) A sequence alignment of the C-terminal domains of ISWI subfamily ATPases illustrates the conserved, positively charged residues (highlighted by blue dots) that are likely to interact with DNA. Conserved domains are indicated by colored bars below the sequence alignment. The regions that cross-link to the entry/exit site of the nucleosome (positions 60 to 62) and the extranucleosomal DNA (position 92) are boxed in brown and cyan, respectively.