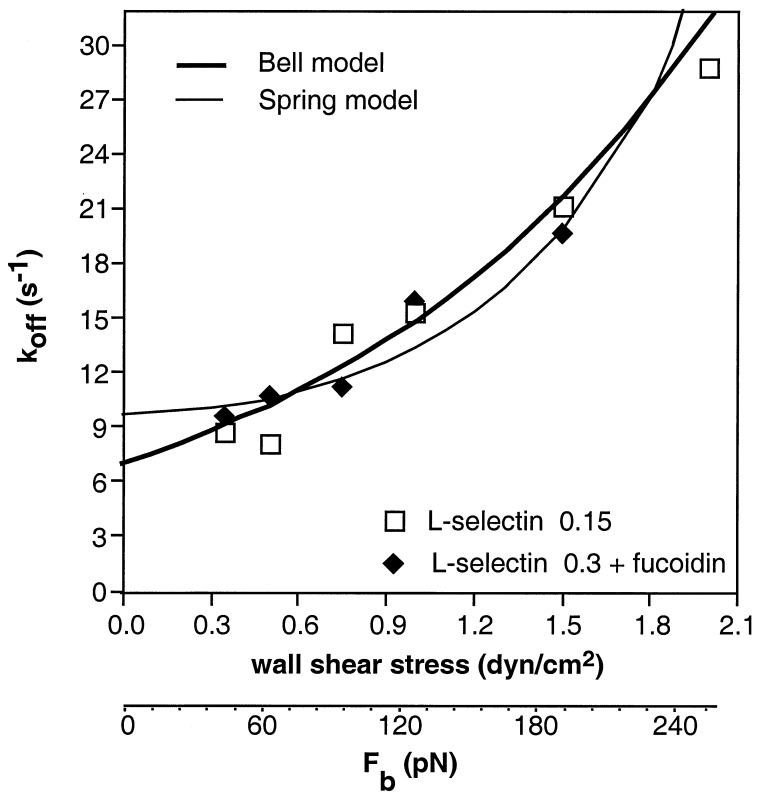
Figure 5.
The increased kinetics of L-selectin transient tether dissociation at increased wall shear stress and force on the tether bond. The koff values at different shear stresses were determined from neutrophil first order dissociation rate constants measured as in Fig. 4. The thick line is the fit of Bell’s equation to all experimental points: koff = k°off exp (σFb/kT), where k°off is the unstressed koff, σ is the separation between receptor and ligand that weakens the bond enough to increase koff by e, k is Boltzmann’s constant, and T is the absolute temperature (29). The thin line is the fit to an Hookean spring model (13, 30): koff = k°off exp (fκFb/2κkT), where κ is the spring constant for the tether bond and fκ is the fraction of the bond spring constant devoted to bond dissociation, also known as the fractional spring slippage (30). This fit yields k°off = 9.7 ± 0.66 sec−1, κ/fκ = 6.31 ± 0.96 N/m. Data was fit by using the program igor (WaveMetrics, Lake Oswego, OR).