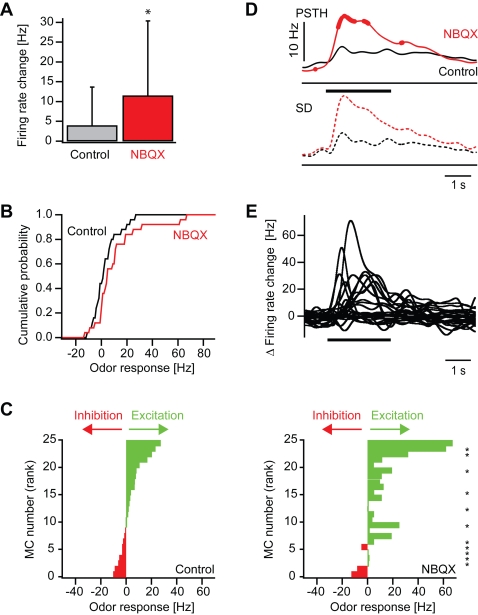
Figure 4. Effect of NBQX on odor responses of mitral cells: quantitative analysis.
(A) Mean firing rate change evoked by odor stimulation before (control) and during NBQX treatment in the time window between 0.25 and 0.75 s after response onset. Error bars show standard deviation. *, P = 0.02 (sign test). (B) Cumulative distribution of odor-evoked firing rate changes in mitral cells before (control) and during NBQX application. (C) Left: mitral cell odor responses ranked according to the firing rate change measured before NBQX application. Right: Responses of the same mitral cells to the same odors in the presence of NBQX (same rank order as control). Asterisks denote responses that were significantly changed in the presence of NBQX (Student's t-test; P<0.05). (D) Top (continuous lines): average peri-stimulus time histogram of mitral cell odor responses before (control) and during NBQX treatment. Thick portions depict time bins where the peri-stimulus time histogram in the presence of NBQX was significantly different from the control peri-stimulus time histogram in the corresponding time bin (sign test; P<0.05). Dashed lines show standard deviation. (E) Differences of peri-stimulus time histograms (NBQX–control) for all mitral cell odor responses.