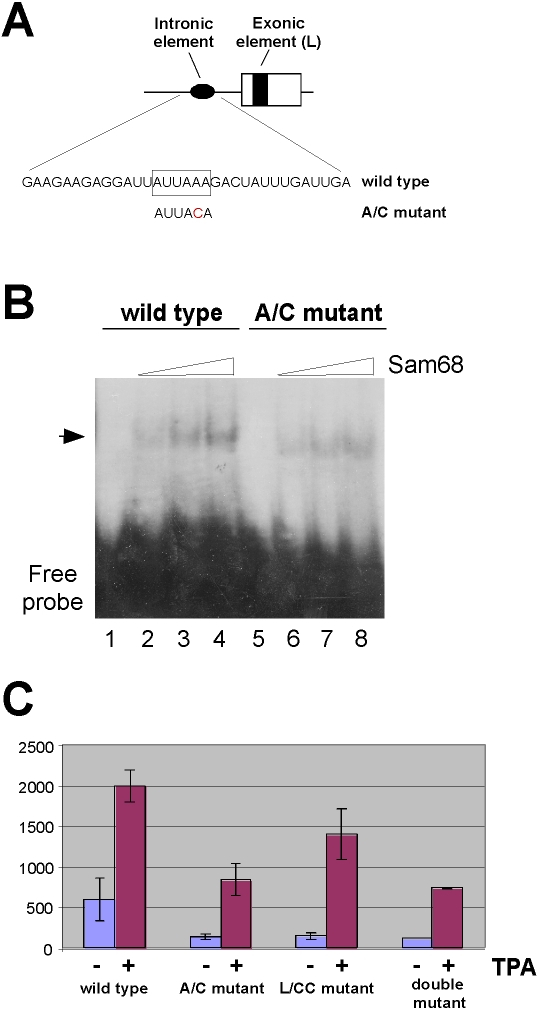
Figure 2. Intronic and exonic Sam68 binding sites affect CD44 v5 exon inclusion.
(A) Scheme indicating positions of the Sam68 binding sites (black oval and box, respectively) in CD44 exon v5 (open box) and the upstream intron (line). The Sam68 consensus binding site in the wild-type RNA sequence used for the electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) in panel B is boxed. The mutated nucleotide of the A/C mutant is indicated in red. (B) EMSA using recombinant Sam68 and radioactively labeled RNA oligonucleotide probes comprising either the wild-type or the A/C-mutant version of the intronic Sam68 binding site (see panel A). (C) v5-luciferase fusion activity from LB17 lymphoma cells transfected with different pETv5luc splice-reporter genes [15]. They were mutated for either the exonic (L/CC mutant [19]), the intronic (A/C mutant), or both Sam68 binding sites (double mutant). Cells were treated with 12-o-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA, 40 ngml−1) (+) or with DMSO (solvent control) (−) for 6h prior to lysis and measurement of luciferase activity. Error bars indicate standard deviations from three independent transfections.